Credit: CC0 Public Domain
A collaboration between the Griffith Institute for Drug Discovery (GRIDD) and multiple clinical research institutes has led to an exciting discovery in cancer research.
The multi-disciplinary team, led by GRIDD's Dr. Alexandre Cristino and Professor Maher Gandhi from Mater Research and including researchers from the Translational Research Institute, discovered a new mechanism in which the Epstein-Barr virus—which can cause lymphoma and blood cancers—escapes the immune system.
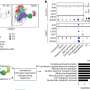
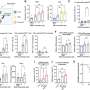
The findings show how viral small RNA regulate the expression of immune-checkpoints, which are proteins that can stop the immune system attacking cancer cells.
"One of the most promising forms of immunotherapy at the moment is inhibiting checkpoint proteins, enabling immune cells to recognize and destroy cancer cells," Dr. Cristino said.
"We're hoping our findings can lead to treatments for lymphomas and blood cancers which are not responding to conventional first-line immunotherapies."
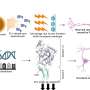
After an extensive research process the team discovered a novel mechanism by which a viral small RNA (miR-BHRF1-2 encoded in the Epstein-Barr virus or EBV genome) regulates the expression of immune-checkpoints ligand PD-L1 and PD-L2 in EBV-positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL).
The discovery may enable potential novel RNA-based treatment therapies to emerge in the future that will work to switch off checkpoint proteins to enhance the body's natural anti-tumoral immunity.
It continues the work being done across the world on immune boosting treatments to fight cancers.
The research has been published in Blood.
More information: Alexandre S Cristino et al. EBV-microRNA-BHRF1-2-5p targets the 3'UTR of immune-checkpoint ligands PD-L1 and PD-L2, Blood (2019). DOI: 10.1182/blood.2019000889
Journal information: Blood
Provided by Griffith University