Breast cancer cells swallow a 'free lunch' of dietary fat particles from the bloodstream
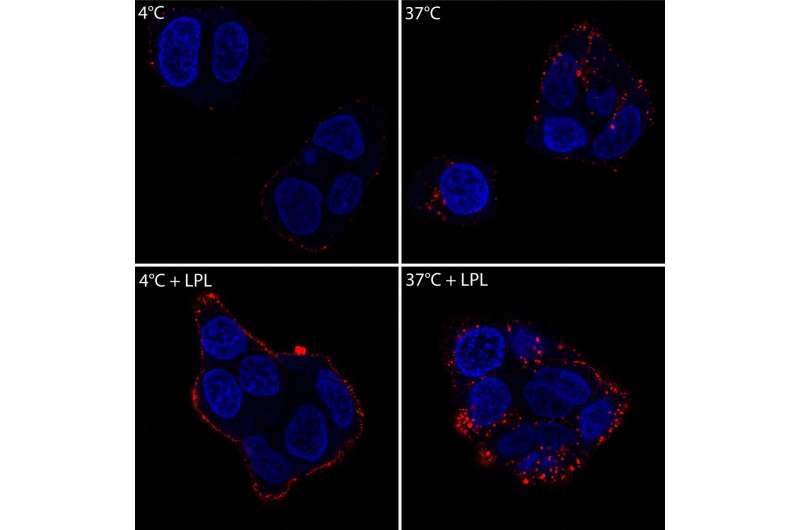
High-fat diets and obesity have been shown to increase the risk of breast cancer and worsen outcomes and prognosis of breast cancer patients. A team of researchers from Dartmouth and Dartmouth-Hitchcock Norris Cotton Cancer Center led by William Kinlaw III, MD, sought to understand how fat from the diet might influence breast cancer cells. In their new study, they found that in addition to making new fat to fuel proliferation, breast cancer cells can take up large quantities of fat derived from the lipid-rich particles that circulate in the bloodstream. The particles bind to the breast cancer cell surface and are then taken into the cell by a novel mechanism not previously described in cancer cells. This uptake provides a large supply of fat that drives proliferation of the cancer cells. Their findings, "Endocytosis of very low-density lipoproteins: an unexpected mechanism for lipid acquisition by breast cancer cells" is newly in press at the Journal of Lipid Research.
"We previously showed that fatty particles in the bloodstream may augment the growth of breast cancer cells," says Kinlaw. "Our new work demonstrates that breast cancer cells can engulf large amounts of preformed fat from the blood using an unexpected mechanism of fat particle uptake called 'endocytosis of lipoproteins'." The uptake results in metabolic reprogramming of the cells to take advantage of this "free lunch" and reveals a direct connection between dietary fat and cancer cell biology.
The literature has also largely focused on manufacture of new fat by cancer cells as a therapeutic target. Many academic- and pharma-based efforts are underway to target the synthesis of new fat by cancer cells. Kinlaw's work shows that "breast cancer cells can evade being killed by drugs that inhibit fat synthesis by simply taking up more exogenous fat particles," he explains. The team's next publication will detail the impact of high fat diets on breast cancer biology in vivo, using mouse models.
More information: Leslie E. Lupien et al, Endocytosis of very low-density lipoproteins: an unexpected mechanism for lipid acquisition by breast cancer cells, Journal of Lipid Research (2019). DOI: 10.1194/jlr.RA119000327