How to take your pulse
Your pulse is your heart rate, or the number of times your heart beats in one minute. You can take your pulse using the radial artery in your wrist or the carotid artery in your neck.
Some medical conditions can be a factor in determining the best place for you to take your pulse. For example, if you have heart disease or longstanding diabetes, it's best to use the artery on your wrist.
General instructions for taking your pulse
To get an accurate pulse:
Take your pulse the same time each day.
Sit down and rest several minutes before taking your pulse.
Count your pulse for a full 60 seconds unless told otherwise by your health care provider.
Taking your radial pulse
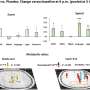
With your palm up, look at the area between your wrist bone and the tendon on the thumb side of your wrist. Your radial pulse can be taken on either wrist.
Use the tip of the index and third fingers of your other hand to feel the pulse in your radial artery between your wrist bone and the tendon on the thumb side of your wrist.
Apply just enough pressure so you can feel each beat. Do not push too hard or you will obstruct the blood flow.
Watch the second hand on your watch or a clock as you count how many times you feel your pulse.
Record your pulse rate.
Taking your carotid pulse
Find the area on one side of your neck near your windpipe. Your carotid pulse can be taken on either side of your neck.
Put the tip of your index and long finger in the groove of your neck along your windpipe to feel the pulse in your carotid artery. Do not press on the carotid artery on both sides of your neck at the same time. This may cause you to feel lightheaded or dizzy, or possibly faint.
Apply just enough pressure so you can feel each beat. Do not push too hard or you will obstruct the blood flow.
Watch the second hand on your watch or a clock as you count how many times you feel your pulse.
Record your pulse rate.
©2020 Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research
Distributed by Tribune Content Agency, LLC.