Loneliness did not appear to increase during pandemic: study

Contrary to expectations, the social (physical) distancing recommendations and stay-at-home orders put in place across the United States to contain the spread of the COVID-19 pandemic did not lead to an uptick in loneliness among Americans, according to research published by the American Psychological Association.
"We were surprised by the overall remarkable resilience in response to COVID-19," said Martina Luchetti, Ph.D., an assistant professor at the Florida State University College of Medicine and lead author of the study published in the journal American Psychologist. "The pandemic is something that everyone is going through, and just knowing that you are not alone and that everyone is going through the same restrictions and difficulties may be enough in the short term to keep feelings of loneliness down."
Even before the pandemic, loneliness was widespread and considered a public health issue in the United States, according to Luchetti. Previous research has associated it with an increased risk of physical health problems and even premature death.
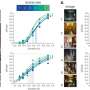
Luchetti and her colleagues had originally surveyed a nationally representative sample of American adults in late January to early February 2020, before the COVID-19 outbreak, as part of a study on loneliness, personality and health. When physical distancing recommendations went into effect in March, the researchers decided to resurvey the participants to find out whether their loneliness levels had increased. Participants completed a second wave of surveys in late March, during the White House's "15 Days to Slow the Spread" campaign, which recommended distancing measures and advised older adults and those with preexisting conditions to quarantine themselves. They completed a third wave of surveys in late April, when most state and local governments had issued stay-at-home orders. Overall, 1,545 participants ages 18 to 98 completed all three surveys; 55% of respondents were men and 45% were women.
Surprisingly, the researchers found no significant change in mean levels of loneliness across the three survey waves. People in at-risk groups, including those living alone and those with chronic health conditions, reported feeling lonelier than others in the first, prepandemic survey, but their loneliness levels did not increase during physical distancing or stay-at-home measures. Older adults' loneliness increased slightly in March but leveled off in April.
The researchers also found that, on average, participants reported increased feelings of social and emotional support during the pandemic. That suggests that for many people, reaching out to friends and family via phone calls, video chats and other physically distant means may have provided an important buffer against loneliness, according to Luchetti.
"Individuals, families and communities can still come together and feel emotionally close despite the physical distancing," she said.
Although there was no average change in loneliness due to physical distancing measures, there may have been individual-level changes, Luchetti cautioned. Some people might become more lonely and others less lonely during the pandemic, she said. Further research could help identify the specific factors that put individuals at risk of loneliness as the world faces the potential of more COVID-19 closures in the future.
More information: The Trajectory of Loneliness in Response to COVID-19. American Psychologist. DOI: 10.1037/amp0000690