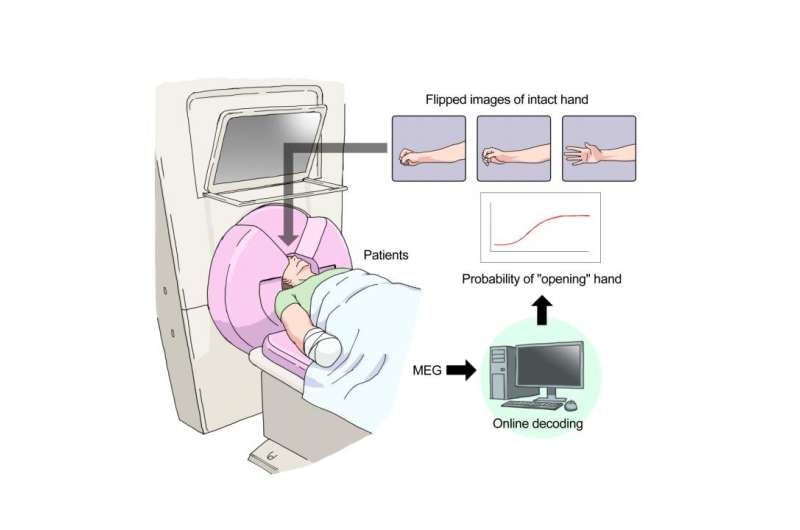
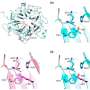
During training, MEG signals were recorded while patients watched the images of the phantom hand that was controlled by real-time decoding of the recorded MEG signals. Credit: Osaka University
Phantom-limb pain is as mysterious as the name implies. The vast majority of amputees experience "phantom-limb" sensations that make them feel their missing limb is still part of their body. The cause is still unknown, and in 50 to 80% of cases, the sensations are painful. With no established treatments or medication, phantom-limb pain can have a large impact on the quality of life and recovery for amputees.
Although the cause is unknown, one theory is that it happens when areas of the brain that used to control the amputated limb remain strongly connected to the mental image of the limb. To weaken this connection, one idea is to train the brain regions that control the intact limb to also control the phantom limb. Takufumi Yanagisawa and his team at Osaka University hypothesized that the key to accomplishing this was to do it unconsciously.
"It is very difficult to intentionally activate the part of your brain that controls your right hand without actually thinking about moving that hand," explains Yanagisawa. "Instead, we designed a system in which the patients did not even know they were using those parts of their brains."
In order to train the brains of patients with phantom-hand pain, the group used a brain-computer interface. First, they recorded brain activity when patients opened and closed their intact hands and used the pattern of brain activity as a template. Then they continuously recorded brain activity related to the intact hands, but asked the patients to try to control a virtual hand with their phantom hand. For half the experiments, this training was real; the recorded brain activity was decoded based on the template and the image of the opening/closing virtual hand was adjusted accordingly. For the other half, the images of the virtual hand were randomly adjusted with no connection to brain activity. All patients thought they were actually controlling the virtual hand. Patients trained for about 30 min/day for three days, and after each session, they rated the intensity of their phantom-limb pain.
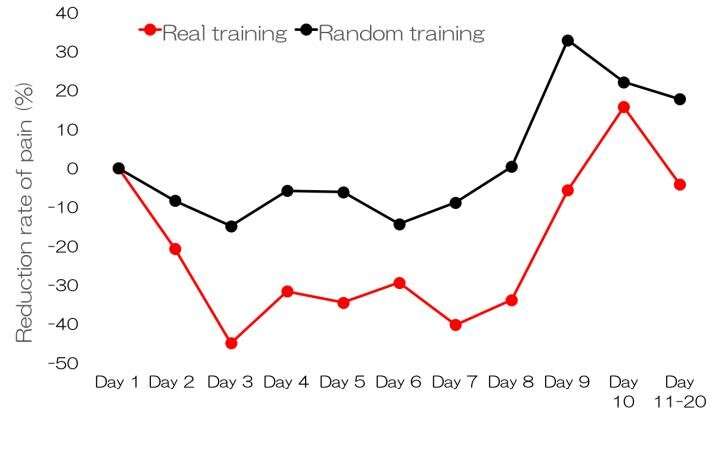
The rate of pain reduction is shown for each day relative to the pain on day 1. Credit: Osaka University
The team found that pain was reduced by 30%, even on the first day of training, and the effect lasted up to five days after training was complete. Importantly, only patients who received real training reported less phantom pain. They also found that after training, the mental image of the phantom hand was weakened in the brain regions that once controlled the amputated hand.
"These findings are promising," says Yanagisawa, "especially given that alternatives like mirror training require a month of training to have the same effect. However, in order for this treatment to become truly practical, the cost must be reduced."
More information: Takufumi Yanagisawa et al, BCI training to move a virtual hand reduces phantom limb pain, Neurology (2020). DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000009858
Journal information: Neurology
Provided by Osaka University