Survival rates of extremely premature babies in Australia rises 20%
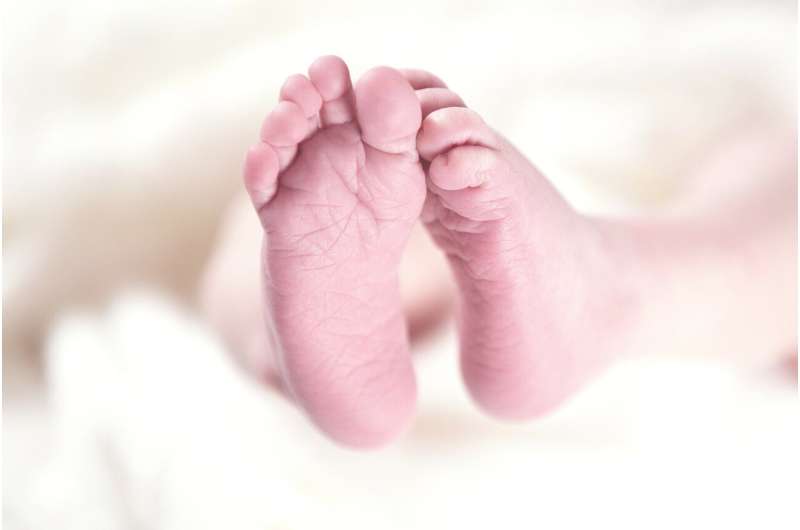

New evidence from a world-leading study in Victoria following premature babies into childhood has shown that survival rates of extremely premature babies has gone up by nearly 20 percent since the early 1990s, thanks to advances in clinical practice, research and technology.
In a paper published in BMJ Open, evidence from the Victorian Infant Collaborative Study (VICS), led by the Royal Women's Hospital, also found that extremely premature babies stayed on breathing support for three times as long as they did in the early 1990s—an outcome of the new ways in which clinicians are now helping babies breathe.
- Survival to discharge home increased (68% (1991-92) to 87% (2016-17))
- Median duration of breathing support increased from 22 days (1991-92) to 66 days (2016-17)
- 1,001 babies born extremely preterm (22-27 weeks' gestation) at four Victorian tertiary hospitals over the past 25 years have taken part.
This is the latest in a collection of VICS sub-studies contributing to state-wide guidelines for clinicians in providing care for extremely premature babies, due to be published in the coming months.
Professor Jeanie Cheong, who leads the study and is a neonatologist at the Women's, said the evidence represents the success of the clinicians who over time have been able to help more of the tiniest and sickest of babies.
"Data from the past 25 years has allowed us to look at how, over time, care has improved for Victoria's youngest and most vulnerable patients—and survival rates have gone up. The introductions of technology such as nasal high flow—a non-invasive breathing treatment for babies—and the associated research by clinicians at the Women's, mark major steps forward in neonatal care. It's the new technologies and research that give our clinicians the confidence to give these babies a fighting chance in the delivery room. At the Women's we see more than 2,000 babies admitted to our neonatal intensive care unit and special care every year—these are the babies who are born too soon, too small or need additional care. Many of these families generously choose to be part of our research, and it's with their help over the years that we are able to translate the findings into improved clinical care."
The Victorian Infant Collaborative Study (VICS) is a long-term study of prematurely born infants throughout their childhood and into adulthood. VICS is a collaboration between the Royal Women's Hospital, Mercy Hospital for Women, Monash Medical Center and the Royal Children's Hospital. For over three decades VICS has been working towards better understanding the extent of long-term health problems that occur in the tiniest babies. The longitudinal study conducts assessments to track the health and wellbeing of children and adults born premature
The sub-study, titled "Changing consumption of resources for respiratory support and short-term outcomes in four consecutive geographical cohorts of infants born extremely preterm over 25 years since the early 1990s," is live now.
More information: Jeanie L Y Cheong et al. Changing consumption of resources for respiratory support and short-term outcomes in four consecutive geographical cohorts of infants born extremely preterm over 25 years since the early 1990s, BMJ Open (2020). DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2020-037507