Credit: University of Sheffield
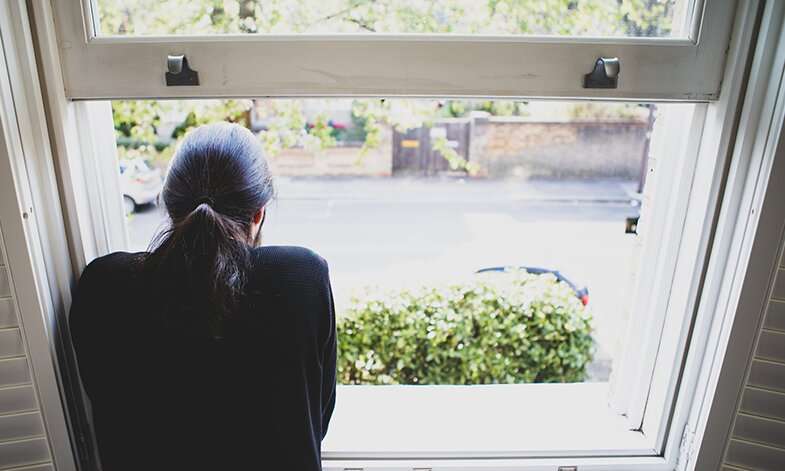
There was a three-fold increase in the number of people reporting significant depression and anxiety problems during lockdown, a study involving scientists from the University of Sheffield has found.
The research revealed that during the coronavirus lockdown in April, the proportion of people reporting clinically significant depression and anxiety problems reached 52 percent, three times more than the pre COVID-19 average of 17 percent.
The international team of experts from universities in three countries also highlighted regional variations in psychological wellbeing which show that socioeconomically deprived areas of the UK reported more severe levels of depression.
The findings, published in the journal Psychosomatic Medicine, also show that the mental health impacts of the pandemic were especially pronounced in younger people, women and those who were unemployed or on low income.
Dr. Jaime Delgadillo, from the Department of Psychology at the University of Sheffield and Director of Psychological Therapies Research at Rotherham Doncaster and South Humber NHS Foundation Trust, said: "We are drawing attention to an urgent problem concerning the mental health of the nation. Historically, mental health care has been underfunded. Mental health problems are very serious health conditions that can become highly disabling if left untreated. This evidence calls for policy makers and health services to look after the mental health of the population during this challenging time."
Michael Barkham, Professor of Clinical Psychology at the University of Sheffield, said: "This study is a detailed investigation of mental health and wellbeing indicators in a representative sample of the UK population during the height of lockdown restrictions. The three-fold increase we found in the prevalence of depression and anxiety problems in the adult population during lockdown is evidence that COVID-19 is associated with a mental health crisis."
Dr. Christoph Pieh, chief investigator based at Donau-Universität Krems in Austria, said: "As COVID-19 is a new disease, and the worldwide lockdown measures are unprecedented for our generation, relatively little is known about the mental health impacts of the current pandemic. We conducted this study to examine several indicators of psychological wellbeing and mental health."
More information: Psychosomatic Medicine (2020). DOI: 10.1097/PSY.0000000000000871
Journal information: Psychosomatic Medicine
Provided by University of Sheffield