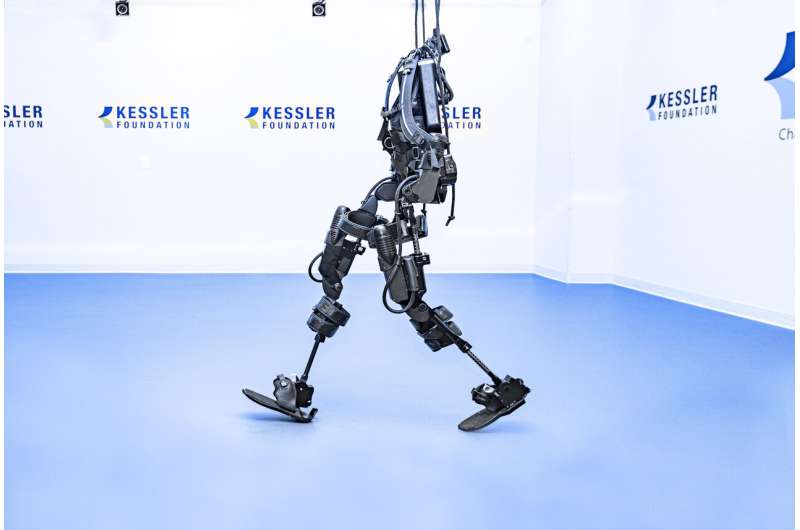
For this study, two types of exoskeletons were used by participants with spinal cord injury - Ekso GT, shown here, and Rewalk. Credit: Kessler Foundation
Exoskeletal-assisted walking is safe, feasible, and effective in individuals disabled by spinal cord injury, according to the results of a federally funded multi-site randomized clinical trial. The article, "Mobility skills with exoskeletal-assisted walking in persons with SCI: Results from a three-center randomized clinical trial" (doi: 10.3389/frobt.2020.00093), was published August 4, 2020 in Frontiers in Robotics and AI.
The authors are Eun-Kyoung Hong, Pierre Asselin, MS, Steven Knezevic, Stephen Kornfeld, DO, and Ann M. Spungen, EdD, of the James J. Peters VA Medical Center, Gail Forrest, Ph.D., of Kessler Foundation, Peter Gorman, MD, and William Scott, Ph.D., of the University of Maryland School of Medicine, and Sandra Wojciehowski, PT, of Craig Hospital and Kessler Foundation. The study was conducted at three sites: James J. Peters VA Medical Center, Bronx, NY; Kessler Foundation, West Orange, NJ; and the University of Maryland.
Study investigators sought to establish guidelines for clinical exoskeletal-assisted walking programs for individuals with spinal cord injury. Their goal was to determine the number of exoskeleton training sessions needed by individuals with varied mobility deficits to gain adequate exoskeletal assisted walking skills and attain velocity milestones. Two powered exoskeletons were used in the study: the Ekso GT (Ekso Bionics), and ReWalk (ReWalk Robotics).
The 50 participants included individuals with tetraplegia and paraplegia, both motor complete and incomplete. In this randomized control trial, their performance was measured over a total of 36 sessions. Participants were randomized to Group 1 (exo-assisted walking) or Group 2 (usual activity) for 12 weeks; each group crossed over to the other study arm. After 12, 24, and 36 sessions, their progress was measured by the 10-meter walk test seconds (s) (10MWT), 6-min walk test meters (m) (6MWT), and the Timed-Up-and-Go (s) (TUG).
The majority of participants mastered the ability to ambulate effectively with the assistance of the exoskeleton, according to Dr. Forrest, director of the Tim and Caroline Reynolds Center for Spinal Stimulation, and associate director of the Center for Mobility and Rehabilitation Engineering Research at Kessler Foundation. After 12 sessions, 31 (62%), 35 (70%), and 36 (72%) participants achieved the milestones established for the 10MWT, 6MWT, and TUG, respectively. After 36 sessions, the results improved, with 40 (80%), 41 (82%), and 42 (84%) of participants meeting the criteria for the 10MWT, 6MWT, and TUG, respectively.
"Participants showed improvement regardless of level of injury, completeness, or duration of injury," noted Dr. Forrest, "indicating that exoskeletons can be used to improve mobility across a broad spectrum of individuals with neurological deficits caused by spinal cord injury. Our results can be used to guide the application of exoskeletons to spinal cord injury rehabilitation, and the timely acquisition of skills for the safe use of these devices for rehabilitation and community use."
More information: EunKyoung Hong et al, Mobility Skills With Exoskeletal-Assisted Walking in Persons With SCI: Results From a Three Center Randomized Clinical Trial, Frontiers in Robotics and AI (2020). DOI: 10.3389/frobt.2020.00093
Provided by Kessler Foundation