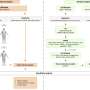
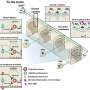
Clinical Decisions Support Tool. Credit: American Gastroenterological Association
Early identification and removal of cancerous colorectal polyps is critical to preventing the progression of colorectal cancer and improving survival rates. The U.S. Multisociety Task Force on Colorectal Cancer has released new guidance for endoscopists on how to assess colorectal lesions for features associated with cancer, discuss how these factors guide management, and outline when to advise surgery after malignant polyp removal.
Key recommendations from the U.S. Multisociety Task Force on Colorectal Cancer, which is comprised of leading experts representing the American College of Gastroenterology (ACG), the American Gastroenterological Association (AGA) and the American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ASGE), include:
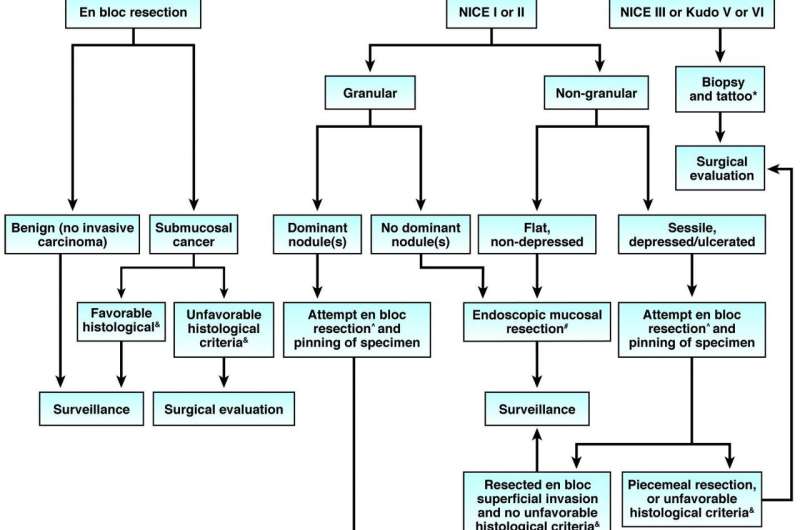
- Management of malignant polyps must begin with a thorough and knowledgeable endoscopic assessment designed to identify features of deep submucosal invasion.
- In nonpedunculated lesions with features of deep submucosal invasion, endoscopic biopsy and tattooing should be followed by surgical resection.
- Nonpedunculated lesions with high risk of superficial submucosal invasion should be considered for en bloc resection and proper specimen handling.
- When pathology reports cancer in a lesion that was completely resected endoscopically, the decision to recommend surgery is based on polyp shape, whether there was en bloc resection and adequate histologic assessment, the presence or absence of unfavorable histologic features, the patient's risk for surgical mortality and morbidity, and patient preferences.
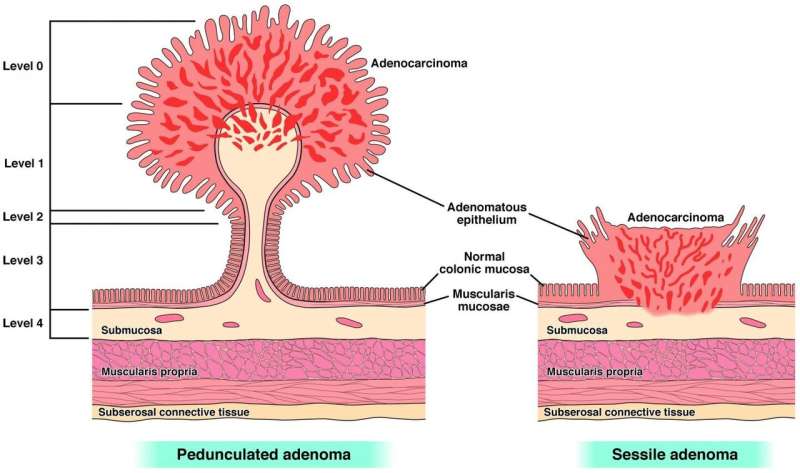
Pedunculated Adenoma and Sessile Adenoma. Credit: American Gastroenterological Association
Provided by American Gastroenterological Association