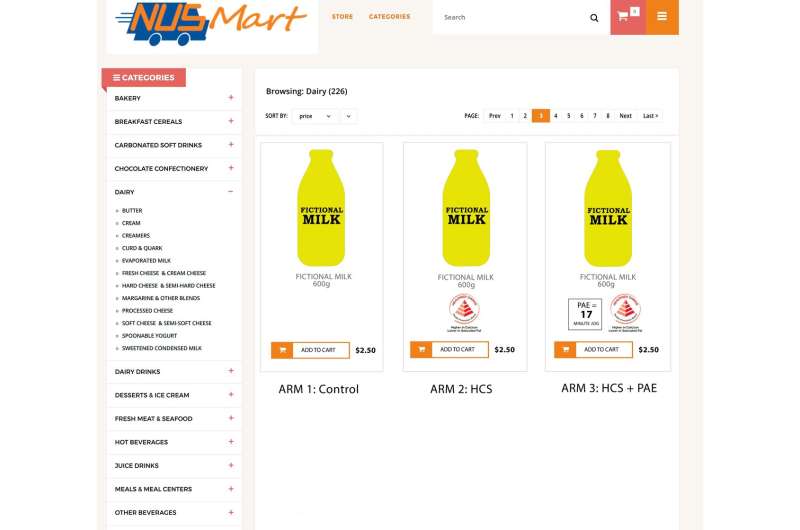
Example product from NUSMart showing how the labels were presented across the three study conditions. NUSMart is an online grocery shopping platform set up by Duke-NUS Medical School researchers to study the impact of changes in the presentation of food and beverage information on consumer choices. It contains thousands of items found in regular stores in Singapore. Credit: Duke-NUS Medical School
Want that packet of biscuits? That'll be 17 minutes of jogging to burn off one serving (and there's probably more than one serving in there).
Such Physical Activity Equivalent (PAE) labels on food and beverages have been shown to encourage consumers to make healthier purchases. However, new research from Duke-NUS Medical School and NUS Saw Swee Hock School of Public Health in Singapore has found that when displayed alongside a Healthier Choice symbol, the positive effects of both labels are diluted. The study was recently published in the journal Appetite.
"Our study shows the importance of keeping labeling simple, so shoppers are not confused or overloaded with information," said Professor Eric Finkelstein, a health economist at Duke-NUS' Health Services and Systems Research Program, who led the study. "With obesity and chronic diseases on the rise globally and in Singapore, it is important to understand what messaging is most effective in helping shoppers choose healthier diets."
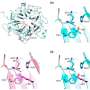
Singapore has been encouraging shoppers to buy food products with the Healthier Choice symbol. The Healthier Choice symbol tells consumers the healthier choices within a food category, such as desserts and sugary beverages, by considering the profile of relevant nutrients of a product in that category (e.g. some products may be healthier due to having lower levels of fat).
Prof Finkelstein and his colleagues hypothesized that showing a PAE label alongside the Healthier Choice symbol would lead shoppers to buy foods and beverages with fewer calories. They recruited more than 100 adults to shop in their online grocery store, NUSMart, which contains thousands of items found in regular stores in Singapore. Participants shopped three times, under different labeling scenarios on certain products: (a) a Healthier Choice symbol, (b) both a Healthier Choice symbol and a PAE label, and (c) no label.
The variants of Healthier Choice Symbol developed, assigned and regulated by Singapore’s Health Promotion Board. Credit: Health Promotion Board, Singapore
They found the Healthier Choice symbol led to a 5% increase in purchasing foods and beverages with that label, showing that it works to influence consumer demand. However, when combined with a PAE label, the effect was diluted. One possible explanation is that the Healthier Choice symbol and the PAE label focus on related but different nutritional aspects of a food product—the former focuses on the overall nutrient profile, whereas the latter focuses more specifically on calories alone.
"These findings show that while the Healthier Choice symbol on its own does encourage Singaporean consumers to purchase healthier products, what is needed for widespread public health impact is a combination of measures to be delivered at sufficient scale across different sectors of the food supply," said Dr. Annie Ling, group director, Policy, Research and Surveillance Division, at Singapore's Health Promotion Board (HPB). Dr. Ling also noted that the findings from this study and from other similar studies have helped HPB to design and refine its policies and programs.
Prof Finkelstein and his colleagues plan to investigate the effectiveness of the new labels with their NUSMart platform, as well as other options, including the potential for shoppers to pick which labels they find most helpful.
"What I have come to believe is that there is no magic bullet the government can use to improve diet quality, but rather a series of nudges that can combine to have meaningful impacts," said Prof Finkelstein, who has studied strategies to reduce obesity rates for more than 20 years.
Professor Rob van Dam, a study co-author from NUS Saw Swee Hock School of Public Health, concurred, "We are excited to conduct high-quality research to identify which messages are most effective to improve dietary choices, and to work with industry and government to improve food labeling and make a real difference in the health of the population."
More information: Finkelstein et al. A Randomized Controlled Trial Testing the Effects of a Positive Front-of-Pack Label With or Without a Physical Activity Equivalent Label on Food Purchases. Appetite (2020). DOI: 10.1016/j.appet.2020.104997
Journal information: Appetite
Provided by Duke-NUS Medical School