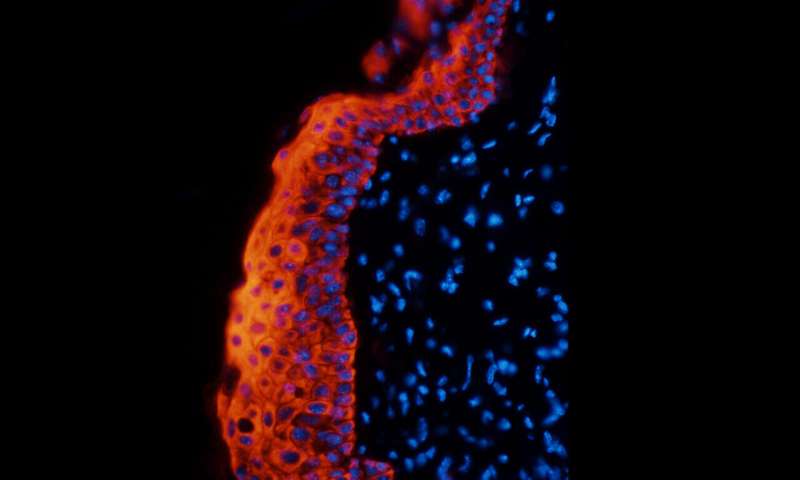
Hallmarks of inflammation. Credit: WEHI
An international team of researchers have uncovered a drug-like compound that blocks a crucial inflammatory pathway, potentially paving the way for a new treatment for a host of diseases—including COVID-19.
WEHI's Associate Professor Seth Masters and his research team discovered the compound could prevent up-regulation of CD14, a key inflammatory protein. The discovery was recently published in EBioMedicine.
Targeting inflammation
Inflammation is our body's natural reaction to infection, said Associate Professor Masters. "In the beginning, it helps you fight the infection—but too much inflammation is linked to a range of chronic and acute diseases," he said.
In a viral disease such as COVID-19, some patients experience excessive inflammation—called a cytokine storm—which can lead to hospitalization or death. Blocking the CD14 pathway can reduce the severity of many diseases, and potentially save lives.
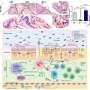
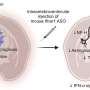
The team focussed their research on a protein called CD14, that is found on certain inflammatory immune cells called macrophages.
"CD14's job is to detect infection, helping to drive inflammation to clear a pathogen. But we know that the amount of CD14 increases on macrophages as inflammation progresses, potentially getting out of control, which could lead to worse outcomes for infections or other diseases," Associate Professor Masters said.
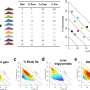
"Our team used CRISPR technology to search for genes that help CD14 levels to rise. We found many really interesting genes that were critical—and when we turned these genes off, they could prevent CD14-driven inflammation from overwhelming the body. Excitingly, a drug-like inhibitor blocks the protein produced by one of these genes. We found this compound could block the rise in CD14 and consequent inflammation in the laboratory, which is incredibly promising," Associate Professor Masters said.
Vital first step towards a treatment
Associate Professor Masters said the discovery of a potential anti-inflammatory compound opened the doors for new anti-inflammatory therapies.
"If this compound could be developed into a safe and effective drug, it could potentially assist in the treatment of many inflammatory diseases. However, once available, the drug would only be beneficial for curbing severe inflammation. Inflammation is a critical process for fighting many infectious, so we only need to use an anti-inflammatory drug for the most severe and life-threatening forms of inflammation," Associate Professor Masters said.
"The next step in this research would be to see if this drug candidate worked against particular diseases in pre-clinical trials. There is great hope this research will one day be translated into an effective treatment for inflammatory illnesses."
The research was supported by a Viertel Senior Medical Research Foundation Fellowship (SLM), the European Union's Horizon 2020 research and innovation program, and the Australian and Victorian governments. GSK funded aspects of the research.
More information: Gisela Jimenez-Duran et al. Pharmacological validation of targets regulating CD14 during macrophage differentiation, EBioMedicine (2020). DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.103039
Journal information: EBioMedicine
Provided by WEHI

.jpg)