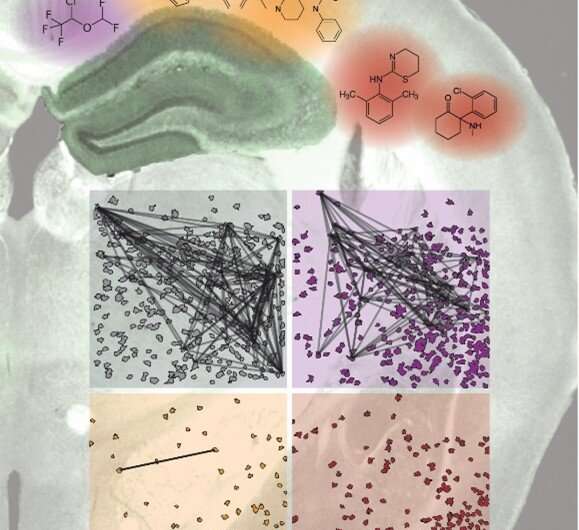
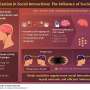
A mouse brain section highlighting the hippocampus is overlaid with the molecular structures of the anesthetics isoflurane (purple), medetomidine/midazolam/fentanyl (orange), and ketamine/xylazine (red). The four panels in the lower part show two-dimensional maps of active neurons in the same hippocampal region during wakefulness (top left) and under the different anesthetics indicated above. Colors indicate the respective anesthetics. Neurons with correlated activity are connected by black lines. Credit: Simon Wiegert, CC-BY
Memory loss is common after general anesthesia, particularly for events occurring immediately before surgery—a phenomenon called retrograde amnesia. But a new study publishing on April 1st 2021 in the open access journal PLOS Biology, led by Simon Wiegert at the University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf in Germany, shows that changes in the hippocampus—the part of the brain used to make new memories—differ depending on which general anesthetic is used. Consequently, their effects on memory formation also differ.
Understanding how different anesthetics affect the brain, particularly the hippocampus, is therefore important for both clinicians with human patients and experimental scientists who work with animals. Wiegert and his team recorded brain activity from the hippocampus while mice were anesthetized using one of three common combinations of general anesthetics: isoflurane, ketamine/xylazine (Keta/Xyl), and medetomidine/midazolam/fentanyl (MMF). Brain activity was recorded electrically and by optically imaging calcium flow—a dynamic signal indirectly reflecting neuronal activity and a trigger that allows brain cells to pass signals to each other.
Both recording methods showed that each drug changed brain activity in the hippocampus compared to wakefulness or natural sleep. The researchers found a number of differences in how the specific anesthetics affected the brain. For example, Keta/Xyl strongly reduced overall calcium activity, while MMF affected its rate much more than the duration. Furthermore, all anesthetics affected the stability of synaptic connections between brain cells in the hippocampus. Keta/Xyl disturbed synaptic stability most drastically, reflecting its strong disturbances of neuronal calcium activity. Recovery time also differed; brain activity returned to normal in about 45 minutes after isoflurane anesthesia, but it took close to 6 hours for the other two drugs. Similarly, the mice showed signs of retrograde amnesia after both Keta/Xyl and MMF anesthesia. But after isoflurane anesthesia—the condition, which showed the mildest disturbances compared to natural sleep—they could still remember what they had learned before the surgery. Knowing these varying effects on the hippocampus and memory formation should be useful for doctors or experimenters when considering which method to use.
Dr. Wiegert notes, "200 million general anesthesia are administered worldwide per year, and amnesia is a central part of it. So, we wondered how it affects the (mouse) hippocampus—a brain region essential for the formation of everyday memories. Surprisingly, the literature is scarce and inconsistent. Therefore, we teamed up with the group of Ileana Hanganu-Opatz and other collaborators to fill this knowledge-gap. Using a large array of experimental methods and developing a number of new analysis routines, we investigated the effects of common anesthetics on the hippocampus at levels ranging from synapses to cellular ensembles and on memory formation. We were surprised to find very distinct short- and long-term effects between the anesthetics used in this study, despite all of them fulfilling the same hallmarks of general anesthesia. Alterations of brain networks in the hippocampus were also different from those described in the neocortex. In summary, our study suggests that isoflurane should be the anesthetic of choice, if brain processes relevant for memory formation should not be disturbed."
More information: Yang W, Chini M, Pöpplau JA, Formozov A, Dieter A, Piechocinski P, et al. (2021) Anesthetics fragment hippocampal network activity, alter spine dynamics, and affect memory consolidation. PLoS Biol 19(4): e3001146. doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.3001146
Journal information: PLoS Biology
Provided by Public Library of Science