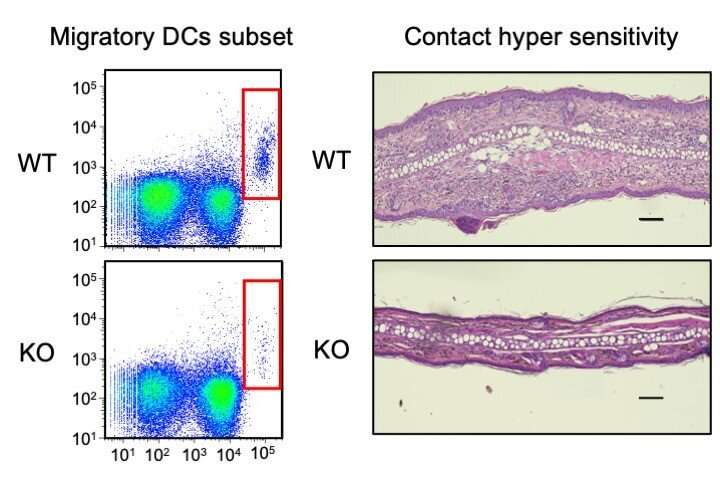
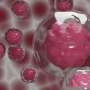
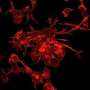
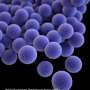
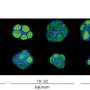
Figure 1. (Left panel) Flow chart demonstrating dendritic cells (DCs) in wildtype (WT) and DC-specific Lamtor1-KO mice. In the absence of Lamtor1, skin-draining lymph nodes showed reduced numbers of migratory DCs. (Right panel) Representative images of the skin of WT and Lamtor1-KO mice. In the absence of Lamtor1, the contact dermatitis was impaired due to impaired antigen-specific immune response. Credit: Osaka University
In a new study, researchers from Osaka University discovered a novel molecular mechanism by which immune cells migrate to fight off infections. These findings may help in understanding the development of certain immune deficiency disorders and establish novel therapies against them.
Immune cells represent a diverse group of cells. Some circulate in the blood stream and migrate to infected tissues after receiving signals from damaged tissues. Others reside in tissues to take up the invading microbe, migrate to lymph nodes and activate an immune response. Therefore, to function effectively, the immune system's activities rely on motile cells. Immune cells move around the body via a process of repeated contraction and expansion, called actomyosin movement, involving myosin proteins. However, how this process of immune cell motility is governed remains unknown.
"As simple as it sounds, cell migration is a highly regulated and complex process," says first author of the study Takeshi Nakatani. "A lot of individual pieces of the cell have to come together to allow immune cells to move forward and travel to infected sites of the body. Lysosomes are compartments within cells that are connected to nutrient sensing and metabolism, and they have also been shown to be involved in cell motility. We wanted to understand how lysosomes regulate the process of immune cell migration."
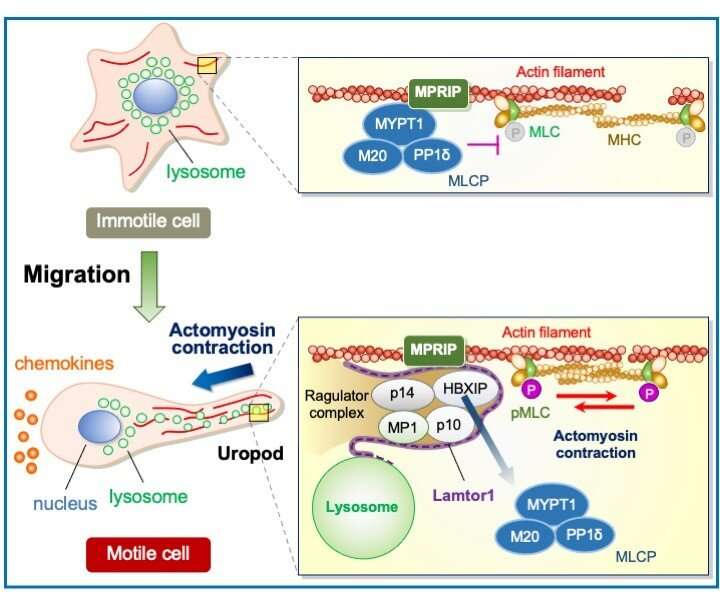
Figure 2. During DC migration, lysosomes are localized to the posterior part of the cell, and the Ragulator complex on the lysosome interacts to MPRIP, which anchors myosin light-chain phosphatase (MLCP) to actin filaments via MYPT1. The interaction between the Ragulator complex and myosin phosphatase Rho-interacting protein (MPRIP) interferes with the interaction between MPRIP and myosin phosphatase–targeting subunit 1 (MYPT1) to release the inhibiting role of MLCP in actomyosin contraction. As a result, actomyosin contraction occurs via phosphorylation of MLC, allowing immune cells to migrate. Credit: Osaka University
The researchers focused on a protein complex on lysosomes, called the Ragulator complex. To understand how the Ragulator complex regulates immune cell motility, the researchers used isolated dendritic cells. These cells take up microbial invaders and bring them to other immune cells in lymph nodes to activate an immune response. The researchers found that when the Ragulator complex interacts with a protein called MPRIP (myosin phosphatase Rho-interacting protein), it prevents the protein MLCP (myosin light chain phosphatase) from blocking the phosphorylation of myosin proteins, resulting in cell contraction. In doing so, the action of the Ragulator complex can be seen as a "brake release."
Interestingly, the researchers found that cells migrate by repeated cycles of protrusions of their front and contraction of their rear, leading to a forward movement. However, in the absence of the Ragulator complex, cell contraction did not occur. In experiments with animals, the researchers found that without the Ragulator complex, dendritic cells cannot travel from peripheral tissue to lymph nodes, which results in an impaired immune response.
"These are striking results that show how the lysosomal Ragulator complex is involved in the migration of immune cells in addition to its functions in cellular metabolism. Our study revealed a novel molecular mechanism by which immune cells migrate and elicit a proper immune response. These findings could help develop novel therapies against autoimmune diseases as well as better vaccines and anti-cancer drugs," says senior author of the study Hyota Takamatsu.
More information: Takeshi Nakatani et al, The lysosomal Ragulator complex plays an essential role in leukocyte trafficking by activating myosin II, Nature Communications (2021). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-23654-3
Journal information: Nature Communications
Provided by Osaka University