Ultrasound brain stimulation slows dementia-related brain degeneration
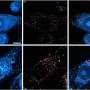
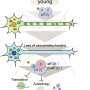
![Brain–behavior correlations. A, Regions of interest—namely left superior parietal lobule (SPL) and left precuneus—where a significant correlation (plotted in panel [B]) was observed between pre-to-post change in cortical thickness and in neuropsychological scores (corrected total score [CTS]). The two regions of interest are highlighted with dotted black contours on lateral and medial views of the DKT atlas parcellation; base image from the Mindboggle project (www.dataverse.harvard.edu/dataverse/mindboggle101). B, Data points in the scatter plot represent patients (N = 17; SPL: green triangles; precuneus: purple squares). Data points sharing the same x value are horizontally jittered by up to 0.25 units to aid visualization. Vertical/horizontal dotted gray lines correspond to no pre-to-post change in terms of neuropsychological score/cortical thickness. “Δ” in the axis labels refers to pre-to-post-TPS change. C, Distribution of neuropsychological (CTS) scores, pre- and post-TPS. Dots represent individual patients, with gray lines connecting values at pre and at post. Horizontal red lines indicate group means. *P Ultrasound brain stimulation slows dementia-related brain degeneration](https://scx1.b-cdn.net/csz/news/800a/2021/ultrasound-brain-stimu.jpg)
The Transcranial Pulse Stimulation with ultrasound (TPS) technique developed at MedUni Vienna under the lead of neuroscientist Roland Beisteiner from the Department of Neurology can be used in various neuropsychiatric brain diseases such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's. It improves brain function by externally activating still-functioning neurons. It has now been demonstrated that TPS can even reduce morphological brain degeneration in dementia patients. The paper has been published in a prestigious medical journal.
In neurological diseases such as Alzheimer's or Parkinson's disease brain neurons are constantly being lost, resulting in memory lapses, speech disorders, mood swings and impaired mobility, for example, as well as muscle tremors in the case of Parkinson's. Treatment options for neurodegenerative diseases are limited and there is currently no cure.
A technique that at least temporarily reduces the breakdown of neurons was developed in Vienna. Transcranial Pulse Stimulation with ultrasound (TPS) is a non-invasive technique that penetrates all areas of the brain and stimulates those neurons that can help to regenerate brain functions. Clinical data from earlier studies showed that two to four weeks of treatment with Transcranial Pulse Stimulation can improve the functional networks and cognitive performance of Alzheimer's patients for up to three months.
Tissue loss is slowed
The recent study has now looked at brain morphology using MRI techniques and has shown that TPS can slow down the cortical atrophy (brain tissue loss) that is typical in Alzheimer's. "We found a significant correlation between neuropsychological improvement and thickness of the cerebral cortex in areas of the brain that are critical in Alzheimer's," explains study leader Roland Beisteiner, who oversaw the development of the new technique of Transcranial Pulse stimulation with ultrasound (TPS) at the Department of Neurology of MedUni Vienna and Vienna General Hospital.
Successful add-on option to supplement current treatments
These results underline the suitability of this technique as an additional option for treating dementia. Due to the effectiveness and attractiveness of the practically side-effect-free technique, several TPS treatment and research centers have already been set up in Europe, North America, and Asia, in addition to MedUni Vienna's Department of Neurology—an Austrian success story, as it were. However, neurological expertise is necessary for low-risk and effective implementation, stresses Beisteiner: "Given the complexity of the technique, it is particularly important from a social perspective that it is used by neuroscientific experts, so that maximum safety and effectiveness can be guaranteed," explains Beisteiner.
More information: Tudor Popescu et al, Transcranial ultrasound pulse stimulation reduces cortical atrophy in Alzheimer's patients: A follow‐up study, Alzheimer's & Dementia: Translational Research & Clinical Interventions (2021). DOI: 10.1002/trc2.12121