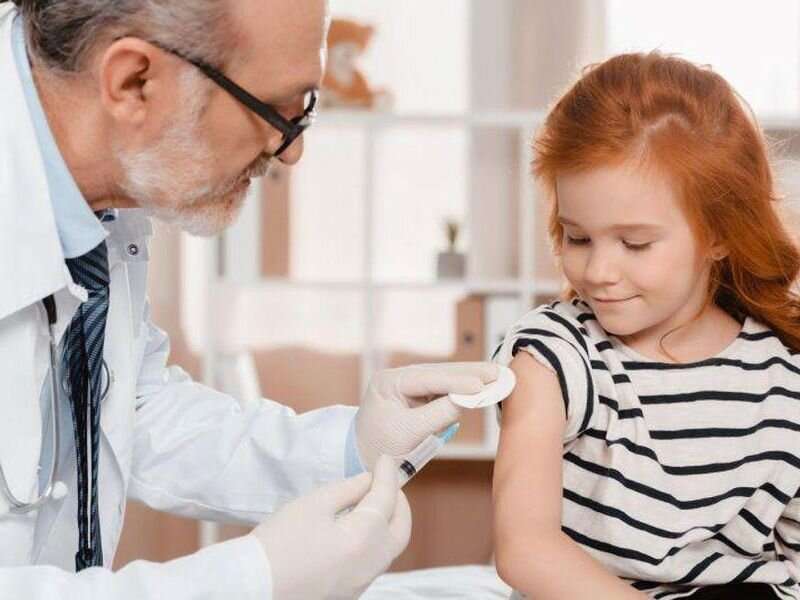
(HealthDay)—A two-dose regimen of 10 μg of BNT162b2 COVID-19 vaccine administered 21 days apart is safe and efficacious in children aged 5 to 11 years, according to a study published online Nov. 9 in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Emmanuel B. Walter, M.D., from the Duke Human Vaccine Institute in Durham, North Carolina, and colleagues presented results for a phase 1, dose-finding study and an ongoing phase 2 to 3 randomized trial involving 5- to 11-year-old children who received two doses of the BNT162b2 vaccine administered 21 days apart.
Forty-eight children received 10, 20, or 30 μg of the BNT162b2 vaccine during the phase 1 study. A dose level of 10 μg was selected on the basis of reactogenicity and immunogenicity. A total of 2,268 children were randomly assigned to BNT162b2 and placebo in the phase 2 to 3 trial (1,517 and 751, respectively). The researchers found that the median follow-up was 2.3 months at data cutoff. As in other age groups, the BNT162b2 had a favorable safety profile in the 5- to 11-year-olds, with no vaccine-related serious adverse events reported. The geometric mean ratio of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 neutralizing titers was 1.04 (95 percent confidence interval, 0.93 to 1.18) for 5- to 11-year-olds versus 16- to 25-year-olds at one month after the second dose, meeting the prespecified immunogenicity success criterion (geometric mean ratio point estimate, ≥0.8). COVID-19 with onset seven or more days after the second dose was reported in three and 16 recipients of BNT162b2 and placebo, respectively (vaccine efficacy, 90.7 percent).
"The data reported herein support vaccination of 5-to-11-year-old children with two 10-μg doses of the BNT162b2 vaccine," the authors write.
Several authors disclosed financial ties to biopharmaceutical companies, including Pfizer and BioNTech, which funded the study.
More information: Abstract/Full Text
Journal information: New England Journal of Medicine
Copyright © 2021 HealthDay. All rights reserved.