Credit: AI-generated image (disclaimer)
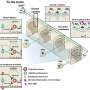
APO-2 (Aposec) is a secretome-based trial preparation derived from stressed peripheral blood mononuclear cells. APO-2 was shown to be safe and effective in a multinational Phase I study in patients with diabetic foot ulcers (non-healing foot ulcers). The Data Safety Monitoring Board has therefore recommended continuation into a Phase II clinical trial. This represents a major success for the wound healing preparation developed at MedUni Vienna.
APO-2 contains the secretome (released substances) of stressed blood mononuclear cells, a current waste product from transfusion units. This new technology harnesses the power of these blood cells, immunology and biotechnology to overcome tissue damage and wound healing disorders. It is produced by the Blood Donor Service of the Upper Austria Red Cross in compliance with Good Manufacturing Practice.
Secretome-based wound healing treatment for diabetic foot ulcers
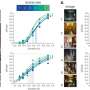
The MARSYAS II clinical trial is the first study to test a secretome-based wound healing treatment in patients with diabetic foot ulcers. APO-2 is applied three times a week for four consecutive weeks. In the main phase (Phase II) of the clinical trial, three different doses of APO-2 are being evaluated. Clinical-stage company Aposcience AG, a MedUni Vienna spin-off, is conducting the study at an international level together with partners FGK Clinical Research GmbH (Munich, Germany) and ABF Pharmaceutical Services GmbH (Vienna).
"Our Phase I study has confirmed that this novel agent is safe for patients with diabetic foot ulcers. Only the data from the Phase II trial will show whether the massive investment in preclinical research and product science has paid off," says Hendrik Jan Ankersmit from the Department of Thoracic Surgery at MedUni Vienna and Vienna General Hospital. The Data Safety Monitoring Board (DSMB) unanimously recommended proceeding with the main phase of the MARSYAS II trial.
The burden of diabetes
According to the International Diabetes Federation, 8.9 percent of adults aged between 20 to 79 in Europe suffered from diabetes in 2019, equating tor 59.3 million people. Another 296,500 children and adolescents under the age of 20 are living with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes is among the top ten causes of non-communicable disease-related deaths. Significant complications of diabetes mellitus are impaired wound healing and the development of foot ulcers. Foot ulcers that do not heal can lead to amputation and premature death.
Provided by Medical University of Vienna