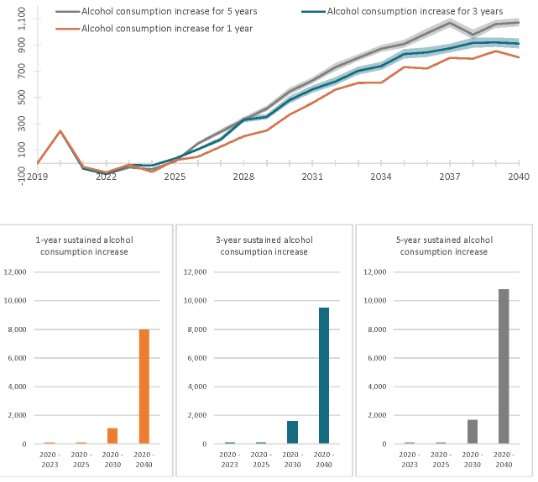
Sensitivity analysis projecting difference in alcohol-related liver mortality and morbidity between a counter-factual scenario and COVID-19 consumption scenario under varying duration of alcohol consumption in adults aged 18+. Annual and cumulative mortality differences between the counter-facture scenario and COVID-19 scenario with sustained increase in alcohol consumption for 1-, 3-, and 5-years. In the base COVID-19 consumption scenario some drinkers increase consumption during the 2020 based on a survey of changes in the US population. Consumption is increased for 1-, 3-, or 5-years and compared to a counter-factual drinking scenario which progresses without any increases associated with COVID-19. Shaded regions represent the 95% uncertainty interval associated with the probabilistic sensitivity analysis. Credit: DOI: 10.1002/hep.32272
Alcohol sales and consumption increased during the start of the COVID-19 pandemic, but the effect of the increase in consumption on population health is not fully understood. In new research published in Hepatology, a team led by investigators at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) projected rates of liver disease and associated deaths due to increased alcohol consumption during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Using data from a national survey of U.S. adults on their drinking habits that found that excessive drinking (such as binge drinking) increased by 21 percent during the COVID-19 pandemic, the scientists simulated the drinking trajectories and liver disease trends in all U.S. adults. They estimated that a one-year increase in alcohol consumption during the COVID-19 pandemic will result in 8,000 additional deaths from alcohol-related liver disease, 18,700 cases of liver failure, and 1,000 cases of liver cancer by 2040. In the short term, alcohol consumption changes due to COVID-19 are expected to cause 100 additional deaths and 2,800 additional cases of liver failure by 2023.
The researchers noted that a sustained increase in alcohol consumption for more than one year could result in 19–35 percent additional mortality.
"Our findings highlight the need for individuals and policymakers to make informed decisions to mitigate the impact of high-risk alcohol drinking during the COVID-19 pandemic in the U.S.," says senior author Jagpreet Chhatwal, Ph.D., associate director of MGH's Institute for Technology Assessment and an assistant professor of radiology at Harvard Medical School.
"While we have projected the expected impact of societal drinking changes associated with the COVID-19 pandemic without any interventions, we hope that our research can help jumpstart needed conversations at every level of society about how we can respond to the many behavioral changes, coping mechanisms, and choices that have short- and long-term implications for the health of individuals, families and communities in America," adds lead author Jovan Julien, MS, a data analyst at the MGH Institute for Technology Assessment and a Ph.D. candidate at the Georgia Institute of Technology.
"The COVID-19 pandemic has had many unintended consequences with unknown long-term impact. Our modeling study provides a framework for quantifying the long-term impact of increased alcohol consumption associated with COVID-19 and initiating conversations for potential interventions," notes co-author Turgay Ayer, Ph.D., the George Family Foundation Early Career Professor of Systems Engineering at Georgia Institute of Technology.
More information: Jovan Julien et al, Effect of Increased Alcohol Consumption During COVID‐19 Pandemic on Alcohol‐related Liver Disease: A Modeling Study, Hepatology (2021). DOI: 10.1002/hep.32272
Journal information: Hepatology
Provided by Massachusetts General Hospital