Credit: The New England Journal of Medicine, DOI: 10.1056/NEJMicm2112363
A 38-year-old male patient complaining of difficulty breathing through one of his nostrils for several years was found to have an ectopic tooth growing in his nose. In their paper published in The New England Journal of Medicine physicians Sagar Khanna and Michael Turner describe how the tooth was identified and what they did to fix the problem.
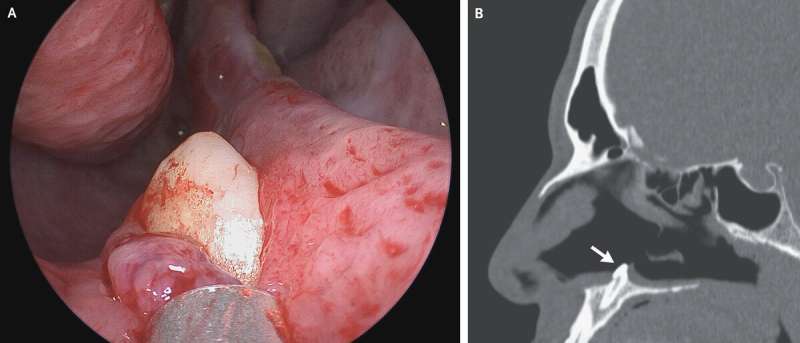
Reports of ectopic body parts are extremely rare. They are defined as body parts growing in places where they normally do not grow. The most common type of ectopic growth involves teeth. And in most cases of ectopic tooth development, a canine is involved. Typically, it grows in the wrong direction in the upper jaw. In this new case, the doctors first found a deviated septum along with calcified septal spurs. After taking a closer look during rhinoscopy, in which a camera is introduced into a nostril, the doctors found what they described as a white object protruding from the wall of the right nostril.
The doctors then opted to X-ray the object and the area around it. The images showed it to be an ectopic tooth that had grown upward from the jaw rather than down into the mouth, as is the usual case. The doctors suggested surgery and the patient agreed. The tooth was extracted with no complications. The patient came back later for a follow-up and doctors found the wound had healed properly and there was no evidence of infection or new tooth growth. Also, the patient reported being able to breathe freely once again.
The doctors note that it is important for people with ectopic body parts to see their doctor—not doing so can result in damage to surrounding tissues. And ectopic teeth can push other teeth out of the way, leading to crooked teeth or gaps. Also, there have been instances of cysts forming on or near such body parts, which can grow to become painful. But the doctors also note that ectopic teeth are extremely rare, occurring in just 0.1% of all people. And it is even more rare for an ectopic tooth to grow all the way up into the nasal cavity or the nose itself.
More information: Sagar Khanna et al, Ectopic Tooth in the Nose, New England Journal of Medicine (2021). DOI: 10.1056/NEJMicm2112363
Journal information: New England Journal of Medicine
© 2021 Science X Network