Screen time tied to behavior problems in children
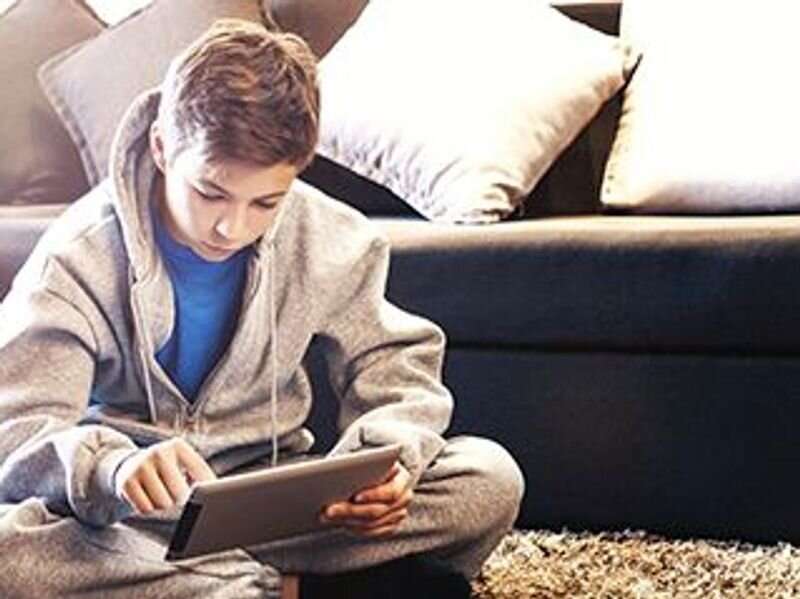

There are small but significant correlations between screen time and behavior problems in children 12 years and younger, according to the results of a systematic review and meta-analysis published online March 16 in JAMA Psychiatry.
Rachel Eirich, from the University of Calgary in Alberta, Canada, and colleagues conducted a systematic literature review to identify studies evaluating the association between the duration of screen time and externalizing and internalizing behavior problems among children (12 years of age and younger).
Based on 87 studies (159,425 participants), the researchers found that increased duration of screen time had a small but significant correlation with more externalizing problems like aggression and inattention (r, 0.11) and internalizing problems like anxiety and depression (r, 0.07) in children. There was evidence of significant between-study heterogeneity (I² = 87.80), which was explained by methodological moderators.
"Our study identified several important methodological moderators of the association between screen time and behavior problems, such as the type of informants and the measures of screen time used, that highlight the lack of harmony in the screen time literature," the authors write. "It is essential for researchers to use more rigorous methods and approaches to analyzing screen time data and to further explore the various facets of screen use (i.e., content and context) associated with children's mental health in a rapidly evolving digital world."
More information: Abstract/Full Text (subscription or payment may be required)
Copyright © 2021 HealthDay. All rights reserved.