Genome-wide screening identified novel targets for treating sorafenib-resistant hepatocellular carcinoma
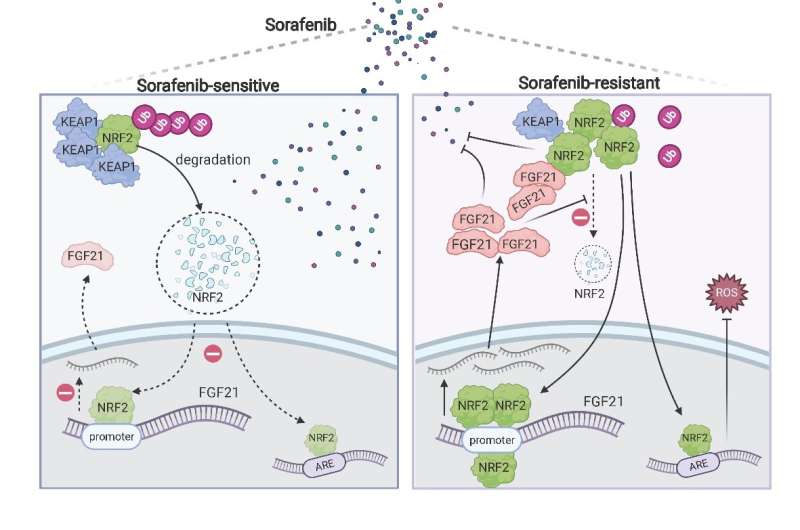
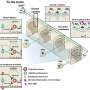
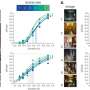
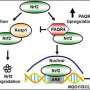
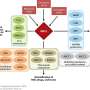
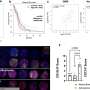
A study led by Xiujun Cai (Department of General Surgery, Sir Run-Run Shaw Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine) screened the whole genome of hepatocellular carcinoma cells (HepG2) through CRISPR / cas9 system under sorafenib treatment, and screened the dominant gene in sorafenib resistance: KEAP1. Nrf2, the downstream molecule regulated by KEAP1, is an important molecule for cells to resist reactive oxygen species (ROS). Firstly, this study verified the function of KEAP1-Nrf2 axis in sorafenib resistance through a large number of functional experiments such as detecting the IC50 of sorafenib in HCC cells with KEAP1/Nrf2 gene editing. This study found that a specific small molecule inhibitor Nrf2 named ML385 could enhance the killing effect of sorafenib both in vivo and in vitro.
Using bioinformatics tools and experimental verification such as qPCR, it was found that FGF21 is the most relevant downstream molecule of Nrf2 in the context of sorafenib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma. Nrf2 positively regulates the expression of FGF21 by using the function of classical transcription factors. Interestingly, this study found that FGF21 can positively regulate the expression of Nrf2 in vivo and in vitro. Further studies found that FGF21 regulates Nrf2 at the protein level, and FGF21 can stabilize its protein by inhibiting the ubiquitination of Nrf2; further experiments such as immunocoprecipitation confirmed that FGF21 binds and stabilizes Nrf2 through the C-terminal of its protein. They constitute a positive feedback regulation pathway. FGF21 plays a role in enhancing its function in KEAP1-Nrf2 pathway, making hepatocellular carcinoma cells acquire the ability to resist sorafenib.
The research was published in Science China Life Sciences.
More information: Jiang Chen et al, CRISPR-Cas9-based genome-wide screening identified novel targets for treating sorafenib-resistant hepatocellular carcinoma: a cross-talk between FGF21 and the NRF2 pathway, Science China Life Sciences (2022). DOI: 10.1007/s11427-021-2067-7