Understanding social networks necessary to tracking spread of disease

Understanding how infectious diseases, such as COVID-19 (causative pathogen—SARS-CoV-2), spread requires a deep understanding of our social connections and networks. It is the way forward for efficient infection prevention and control, according to researchers writing in the International Journal of Medical Engineering and Informatics.
S. Mahadevi, Shyam S. Kamath, and D. Pushparaj Shetty of the Department of Mathematical and Computational Sciences at the National Institute of Technology Karnataka in Surathkal, Mangalore, India, explain that it is important to have effective models of infectious disease, especially those with the potential to cause debilitating global pandemics. The team has used graph energy centrality to study COVID-19 data from South Korea (Korean Centers for Disease Control and Prevention) by building a transmission network from that data and also from the Johns Hopkins University data in the U.S. The team has also used data from Australia, Canada, China, Germany, India, Italy, and elsewhere to help them validate their model.
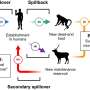
The model allows them to home in on the most active nodes, the likely infectious superspreaders, within the network. If such nodes can be detected in a network before a disease has spread widely, those individuals, and perhaps even sites and events might be put under specific isolation rules to slow if not stave off the emergence of a pandemic. The researchers point out that many of the emergent human infectious diseases arise from wild animal hosts where the native virus or other pathogen is often endemic. A problem commonly arises when humans are interacting closely with those animals or other vectors of disease and the pathogen opportunistically makes the leap from species to species reaching a person who would essentially be Patient 0.
Subsequently, the detection of high-risk hosts is important for the management and monitoring of such diseases, especially the identification of those at risk with wide social networks. This will be critical in the face of the next lethal pandemic.
More information: S. Mahadevi et al, Study of novel COVID-19 data using graph energy centrality: a soft computing approach, International Journal of Medical Engineering and Informatics (2022). DOI: 10.1504/IJMEI.2022.122287