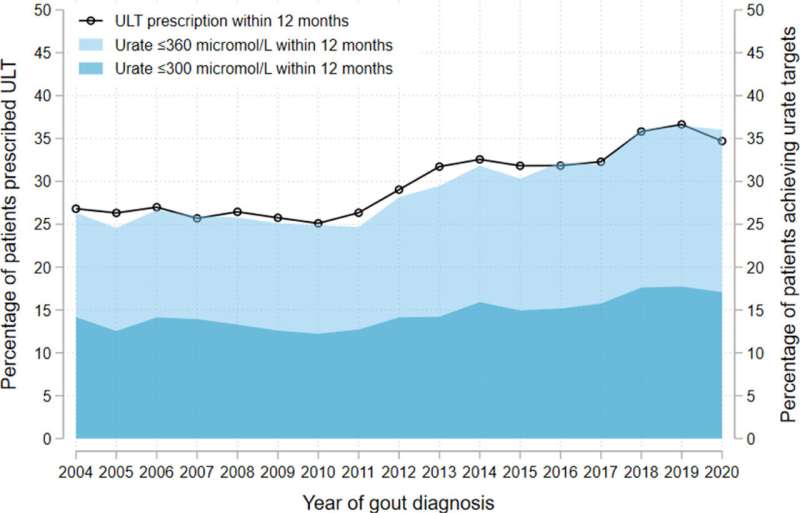
Proportion of patients newly diagnosed with gout (n = 129,972), separated by year of diagnosis, who: i) were initiated on urate-lowering therapy (ULT) within 12 months of diagnosis (black line); or ii) had a serum urate performed (n = 65,127) and attained a level ≤360 µmol/L (light blue) or ≤300 µmol/L (dark blue) within 12 months of diagnosis. Credit: The Lancet Regional Health - Europe (2022). DOI: 10.1016/j.lanepe.2022.100416
Just one in three patients with gout in the U.K. received preventative medication within a year of diagnosis, new research has found. The study is published today in The Lancet Regional Health—Europe by researchers from King's.
Gout is the most common form of inflammatory arthritis in the U.K., affecting 1 in 40 people. People with gout experience recurrent flares of severe joint pain and swelling, which can lead to joint damage and functional impairment if undertreated or not treated at all. Gout is also associated with other conditions, including chronic kidney disease.
In people with gout, flares can be prevented with highly effective, low-cost, urate-lowering medications, such as allopurinol. However, previous studies highlighted that only a minority of people with gout were started on these medications, leaving them at risk of ongoing flares. In 2012, just 27% of people with gout in the U.K. received prescriptions for urate-lowering medications. Because of this, European and British gout management guidelines were updated in 2016 and 2017, to encourage the prescription of these medications.
Researchers from King's used the Clinical Practice Research Datalink, a health database of people registered with more than 2,000 general practices in the U.K., to determine whether care for people with gout had improved since the guidelines were published. They were able to evaluate the management of 129,000 people with newly diagnosed gout in the U.K. between 2004 and 2020.
The results showed only a modest improvement in the prescription of urate-lowering medications over the study period, from 27% of patients diagnosed in 2004, to 37% in 2019. This was followed by a reduction in prescriptions in 2020, with 35% of patients being prescribed medication, which may reflect reduced access to care because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Researchers also showed that just one in six patients achieved the target blood urate level recommended by the British Society for Rheumatology. People with other medical conditions, such as heart failure and kidney disease, were more likely to be prescribed medication than those without co-morbidities, however they were less likely to achieve these target urate levels.
The findings suggest that the quality and success of gout care in the U.K. remain poor despite updated guidelines. This problem is not limited to people with gout who are managed in primary care; other studies have shown that patients managed in specialist clinics frequently do not achieve the target urate levels necessary to prevent flares and damage.
"These results were quite surprising as the initiation of treatment is straightforward, and the medications we use to treat and prevent gout have been around for decades, and are cheap. Our data indicate that we have a lot more work to do. Strategies are needed to encourage the prescription of preventative medications in people with gout. For example, educational programs could help to raise awareness about the importance of medications such as allopurinol in the prevention of recurrent flares and disability due to gout," says Dr. Mark Russell, from the School of Immunology & Microbial Sciences.
Senior author Dr. James Galloway from School of Immunology & Microbial Sciences added: "This study highlights the value of large datasets from primary care, and how applying analytical tools can uncover major challenges with the treatment of what are, in essence, very common inflammatory diseases. Reassuringly, these challenges are not so difficult to fix, and could have a huge impact on tens of thousands of people suffering from this condition across the country."
More information: Mark D Russell et al, Management of gout following 2016/2017 European (EULAR) and British (BSR) guidelines: An interrupted time-series analysis in the United Kingdom, The Lancet Regional Health—Europe (2022). DOI: 10.1016/j.lanepe.2022.100416
Provided by King's College London