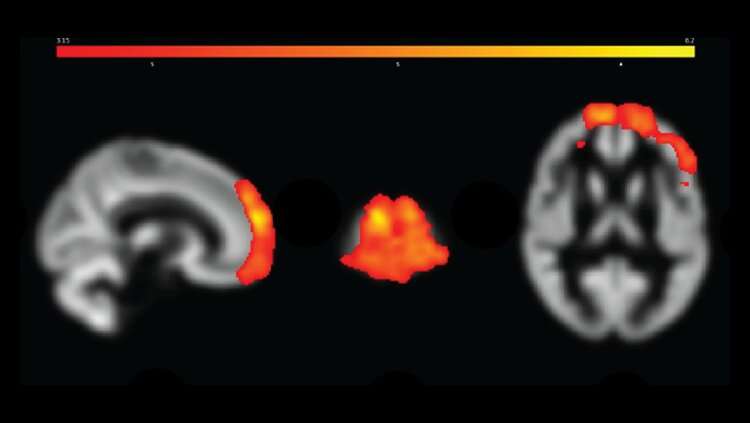
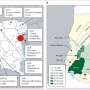
Gulf War Veterans with chronic pain had had lower regional gray matter volume in the left and right insular cortices. Credit: Ninneman et al., JNeurosci 2022
The brains of Gulf War veterans with chronic pain possess larger pain processing regions and smaller pain regulation regions compared to their healthy peers, according to new research published in JNeurosci.
Over one third of Gulf War veterans experience widespread, chronic pain linked to a condition called Gulf War Illness. The underlying cause of the pain is poorly understood, preventing the development of effective treatments. Ninneman et al. analyzed the brains of Gulf War veterans with and without pain using MRI. The participants also completed questionaries about their pain symptoms, fatigue, and mood.
Those with chronic pain displayed smaller left and right insular cortices, two brain areas involved in regulating pain. They also had larger areas of the frontal cortex, specifically in regions involved in pain sensitivity and emotional regulation. The structural changes were more pronounced in people with worse pain, but there was no relationship with fatigue or mood.
These results indicate the chronic pain from Gulf War Illness may stem from changes in how the central nervous system processes pain, rather than with issues with nerves or pain receptors.
More information: Pain, but not Physical Activity, is Associated with Gray Matter Volume Differences in Gulf War Veterans with Chronic Pain, JNeurosci (2022). DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2394-21.2022
Journal information: Journal of Neuroscience
Provided by Society for Neuroscience