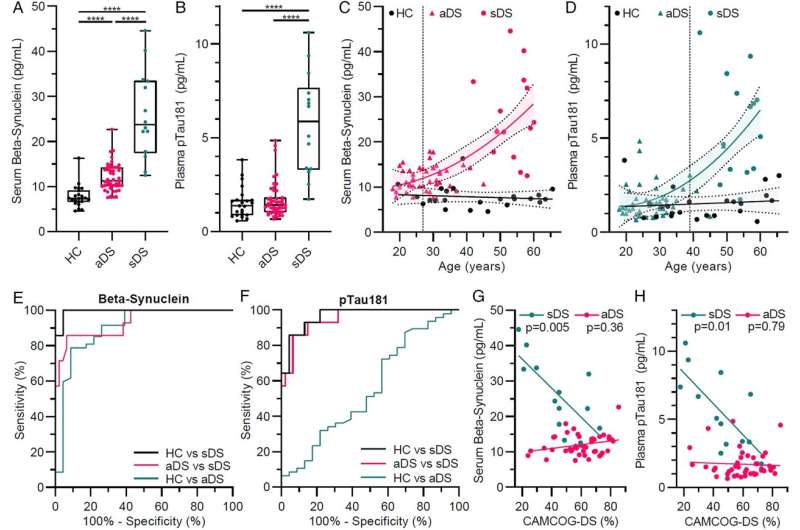
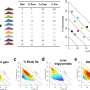
Group comparisons, correlation analyses, and diagnostic performance of serum beta-synuclein and plasma pTau181. (A) Serum beta-synuclein and (B) plasma pTau181 levels were compared between euploid healthy controls without neurological disease (HC, n = 23) and adults with Down syndrome (DS) diagnosed with Alzheimer disease (symptomatic, sDS, n = 14) or without AD (asymptomatic, aDS, n = 47). Groups were compared with multiple linear regression after log2 transformation of biomarker levels and with age and sex as covariates. Boxes are median and interquartile range; whiskers are minimum and maximum. ****p < 0.0001. (C) Scatter plot of serum beta-synuclein and (D) plasma pTau181 levels with age. Linear (HC) and second order polynomial regression (DS) was performed to estimate the time course of biomarker changes indicated by the solid lines (with 95% confidence interval [CI]). The dotted vertical line indicates the age where the two regression lines diverge (point where the 95% CIs no longer overlap). Dots and triangles are individual values. (E, F) Receiver operating characteristic curve analysis of (E) beta-synuclein and (F) pTau181 levels for discrimination of the different groups. Beta-synuclein: HC vs sDS, area under the curve (AUC) = 0.99, 95% CI = 0.98–1.00; aDS vs sDS, AUC = 0.94, 95% CI = 0.85–1.00; HC vs aDS, AUC = 0.90, 95% CI = 0.81–0.99. pTau181: HC vs sDS, AUC = 0.97, 95% CI = 0.92–1.00; aDS vs sDS, AUC = 0.95, 95% CI = 0.90–1.00; HC vs aDS, AUC = 0.55, 95% CI = 0.40–0.70. (G, H) Spearman partial correlation analysis of (G) beta-synuclein and (H) pTau181 levels with achieved number of points relative to the number that could maximally be reached on the Cambridge Cognitive Examination for Older Adults with Down Syndrome (CAMCOG-DS), including age as covariate. Beta-synuclein: aDS, r = 0.15; sDS, r = −0.75. pTau181: aDS, r = 0.04; sDS, r = −0.69. Dots are individual values, and lines are from linear regression. Credit: Annals of Neurology (2022). DOI: 10.1002/ana.26360
Researchers from DZNE and Ulm University Hospital have identified a protein in the blood that may indicate the degradation of neural connections years before the onset of dementia symptoms. If these findings are confirmed, recording this protein called "beta-synuclein" could contribute to the early detection of Alzheimer's disease and possibly also help to assess nerve damage resulting from stroke or traumatic brain injury.
The evidence, published in the journal Annals of Neurology (print edition), is based on studies of 84 adults, including 61 people with Down syndrome. Experts from the LMU Klinikum München and University Medicine Halle (Saale) were also involved in the study.
"Our data suggest that levels of beta-synuclein in the blood rise already in the early stages of Alzheimer's disease and that this is related to the breakdown of neural connections, so-called synapses," explains PD Dr. Patrick Öckl, research group leader at DZNE's Ulm site and at the Department of Neurology at Ulm University Hospital. "So here we have a potential biomarker that could help detect incipient dementia at an early phase—presumably more than ten years before symptoms become manifest." At present, Alzheimer's disease is diagnosed and treated far too late, the scientist notes: "By then, the brain is already massively damaged. We need to start earlier to increase the chances of being able to effectively combat the disease. Beta-synuclein could open up a possibility for this. However, further studies are still needed to confirm our findings."
Down syndrome associated with dementia
The results of the current study are based on examinations of 61 people with Down syndrome (also known as "trisomy 21") and 23 cognitively healthy adults. For this, the Ulm team led by Patrick Öckl cooperated with colleagues from Munich and Halle an der Saale.
"People with Down syndrome are affected by a genetically determined developmental disorder of the brain, which usually results in an impairment of intellectual abilities. In addition, their genome exacerbates molecular processes that are involved in the development of Alzheimer's. Down syndrome is therefore associated with an inherited form of Alzheimer's disease with an early onset of symptoms. Usually, this happens beyond the age of 40," says Prof. Johannes Levin, neurologist at DZNE's Munich site and head of the outpatient clinic at LMU Klinikum München for individuals with Down syndrome and cognitive disorders. "From the study of Down syndrome, we can learn quite a bit about dementia. We assume that the processes that occur here in a particularly pronounced way also happen in individuals who have Alzheimer's but no Down syndrome."
Wide potential for use
If further studies confirm the current findings, various applications could be considered for the beta-synuclein marker: "For drug studies on Alzheimer's disease, a synaptic blood marker would be very helpful to record treatment effects, that is, to determine what an experimental compound does in the brain. This would usefully complement the picture provided by the already established markers," says Prof. Markus Otto, head of the Department of Neurology at University Medicine Halle, who also played a significant role in the current studies. "I see another application in dementia prevention and early detection. The possibility to measure beta-synuclein in blood is much more convenient for patients compared with the currently used analysis of cerebrospinal fluid."
Otto adds: "Considering that synapses are also lost in traumatic brain injury and stroke, the relevance of beta-synuclein is even more far-reaching. In these cases, too, the marker could help assess nerve damage and thus contribute significantly to better diagnostics and therapy."
More information: Patrick Oeckl et al, Serum Beta‐Synuclein Is Higher in Down Syndrome and Precedes Rise of pTau181, Annals of Neurology (2022). DOI: 10.1002/ana.26360
Provided by German Center for Neurodegenerative Diseases