Study explores how belly fat increases risk of metabolic disease

Changes that occur in the body in response to an increase in belly fat have been put under the microscope as part of a study from TwinsUK, offering new insight into the cause of metabolic disease.
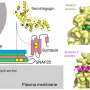
The study, led by King's researchers Dr. Jordana Bell and Colette Christiansen and published in medical journal Genome Medicine, looked at how epigenetic marks (measures of how the human body reads DNA to affect the way genes work) in fat tissue change as belly fat accumulates.
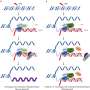
Using samples from 538 TwinsUK participants and combining genetic, gene function, diet, and health data, the researchers examined epigenetic marks across the genome (the complete set of a person's genetic material) and found nine genes that are highly relevant to metabolic disease risk.
Among these was a gene where the identified epigenetic changes were recognized as a potential mechanism through which diet can affect belly fat accumulation, as well as other epigenetic marks that translate genetic risk effects on metabolic health.
The findings also allowed the researchers to characterize the molecular changes that occur because of an increase in belly fat and the impact these changes have on gene function and insulin resistance.
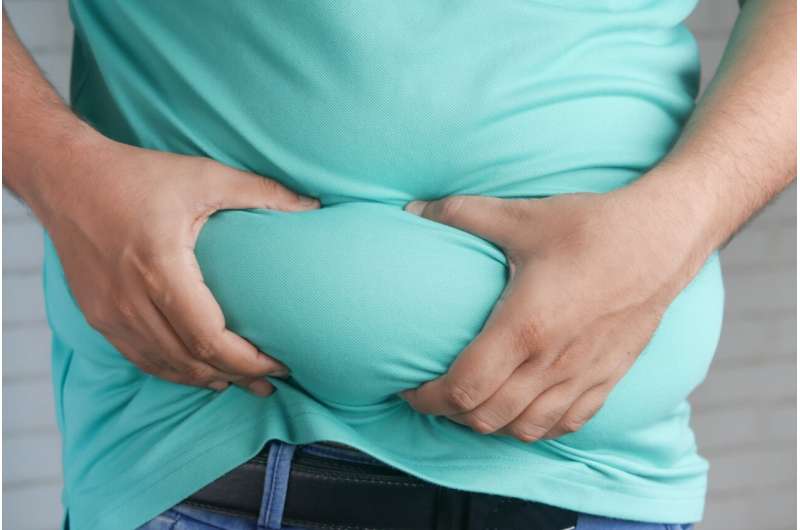
Metabolic diseases—the most common of which is diabetes—disrupt normal metabolism, or the process of converting food to energy on a cellular level. While previous studies in this field have explored the role of epigenetic marks in overall obesity using body mass index (BMI), the build-up of belly fat deep within the abdomen is known to be a greater risk factor for metabolic disease than BMI alone.
"With rapidly rising rates of obesity worldwide, it is important that we understand how elevated body fat affects us at the molecular level and how this translates to metabolic disease risk," said Dr. Bell.
"Our study brings us one step closer to this goal by identifying an epigenetic signature of excess belly fat, understanding its genetic and dietary triggers, and characterizing its functional impacts and clinical consequences for insulin resistance."
Based on the results of the study, the researchers also developed an epigenetic predictor of insulin resistance, relating their findings to the clinical consequences of elevated belly fat.
Colette Christiansen, Ph.D. researcher in the School of Life Course & Population Sciences said, "It is exciting to see that when we combine many different layers of biological information, we can start to unravel the mechanisms which drive the state of our biological health."
More information: Colette Christiansen et al, Adipose methylome integrative-omic analyses reveal genetic and dietary metabolic health drivers and insulin resistance classifiers, Genome Medicine (2022). DOI: 10.1186/s13073-022-01077-z