Financial challenges drive medical decisions for adults with heart disease
A nationally representative study led by Yale researchers reveals that a significant number of U.S. families—two in five—face financial challenges due to atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD), a set of health conditions caused by plaque buildup in arterial walls.
Writing in the journal JAMA Health Forum, the authors conclude that the lack of a systematic measure of financial hardship fails to assess both the burdens faced by these patients and the consequences felt by their families due to delayed or deferred care.
ASCVD, which includes patients with heart attack, stroke, coronary heart disease, or angina, affects nearly 10% of the U.S. adult population.
For the study, the authors explored two strategies for measuring financial hardship due to healthcare expenses: "objective" and "subjective" financial hardships. Objective hardship is described as out-of-pocket medical expenses such as medical equipment, medications, and emergency department visits exceeding 20% of an individual's annual income, while subjective hardship is defined as when a patient has difficulty paying medical bills.
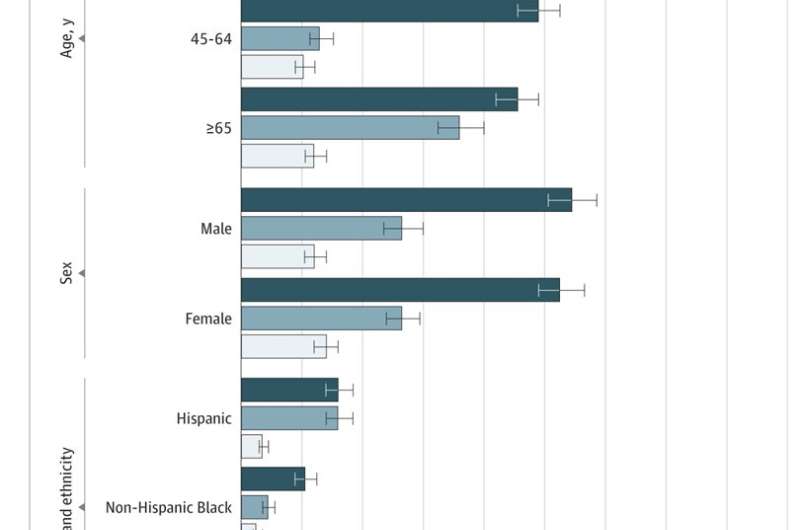
While objective and subjective measures are often used interchangeably to assess care-related hardships, the research team evaluated both using data from the 2014–2018 Medical Expenditure Panel Survey. Among 10,975 families in which at least one member had ASCVD, the researchers found that 37% experienced either subjective or objective financial hardship, a proportion much larger than previously reported in studies focusing on individual measures.
The study's senior author, Dr. Rohan Khera, and his team found that subjective financial hardship was more common. The results showed that one in four families reported subjective financial hardship, whereas just one in 10 experienced objective financial hardship.
Furthermore, 20% of families reported a delay in getting medical care, prescription medications, and/or dental care due to financial challenges. The researchers also found that uninsured individuals or those with public insurance had higher reported challenges with paying medical bills than those with commercial health insurance. Individuals who reported challenges with paying medical bills also represented those more likely to defer or forgo care.
"We used both subjective and objective measures to evaluate patients with ASCVD suffering from financial hardship," said Khera, an assistant professor at Yale School of Medicine. "Emphasizing one of these measures may cause important details to be overlooked, such as those who are deferring health care. Our study provides the basis for a more nuanced approach for measuring the burden healthcare places on our patients and their families.
"We believe that implementing a comprehensive measurement strategy for the effects of healthcare expenses on our patients is essential in routine clinical care, and can help identify an important challenge for our patients, addressing which can improve their health outcomes."
More information: Stephen Y. Wang et al, Measures of Financial Hardship From Health Care Expenses Among Families With a Member With Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease in the US, JAMA Health Forum (2022). DOI: 10.1001/jamahealthforum.2022.1962