Being lonely and unhappy accelerates aging more than smoking, study finds

Molecular damage accumulates and contributes to the development of aging-related frailty and serious diseases. In some people these molecular processes are more intense than in others, a condition commonly referred to as accelerated aging.
Fortunately, the increased pace of aging may be detected before its disastrous consequences manifest by using digital models of aging (aging clocks). Such models can also be used to derive anti-aging therapies on individual and population levels.
According to the latest article published in Aging-US, any anti-aging therapy needs to focus on one's mental health as much as on one's physical health. An international collaboration led by Deep Longevity with US and Chinese scientists has measured the effects of being lonely, having restless sleep, or feeling unhappy on the pace of aging and found it to be significant.
The article features a new aging clock trained and verified with blood and biometric data of 11,914 Chinese adults. This is the first aging clock to be trained exclusively on a Chinese cohort of such volume.
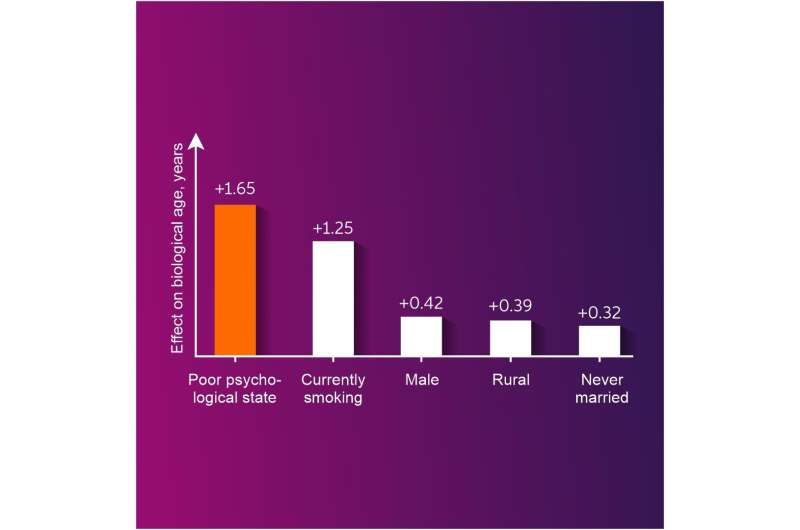
Aging acceleration was detected in people with a history of stroke, liver and lung diseases, smokers, and most interestingly, people in a vulnerable mental state. In fact, feeling hopeless, unhappy, and lonely was shown to increase one's biological age more than smoking. Other factors linked to aging acceleration include being single and living in a rural area (due to the low availability of medical services).
The authors of the article conclude that the psychological aspect of aging should not be neglected either in research or in practical anti-aging applications. According to Manuel Faria from Stanford University, "Mental and psychosocial states are some of the most robust predictors of health outcomes—and quality of life—yet they have largely been omitted from modern health care."
Alex Zhavoronkov, the CEO of Insilico Medicine, points out that the study provides a course of action to "slow down or even reverse psychological aging on a national scale."
Earlier this year, Deep Longevity released an AI-guided mental health web service, FuturSelf.AI, that is based on a preceding publication in Aging-US. The service offers a free psychological assessment that is processed by an AI and provides a comprehensive report on a user's psychological age as well as current and future mental well-being. Deepankar Nayak, the CEO of Deep longevity affirms, "FuturSelf.AI, in combination with the study of older Chinese adults, positions Deep Longevity at the forefront of biogerontological research."
Deep Longevity developed the Longevity as a Service (LaaS) solution to integrate multiple deep biomarkers of aging dubbed "deep aging clocks" to provide a universal multifactorial measure of human biological age.
More information: Psychological and biological aging clocks reveal the main contributors to the aging rate in Chinese older adults, Aging-US (2022). DOI: 10.1000/xyz123