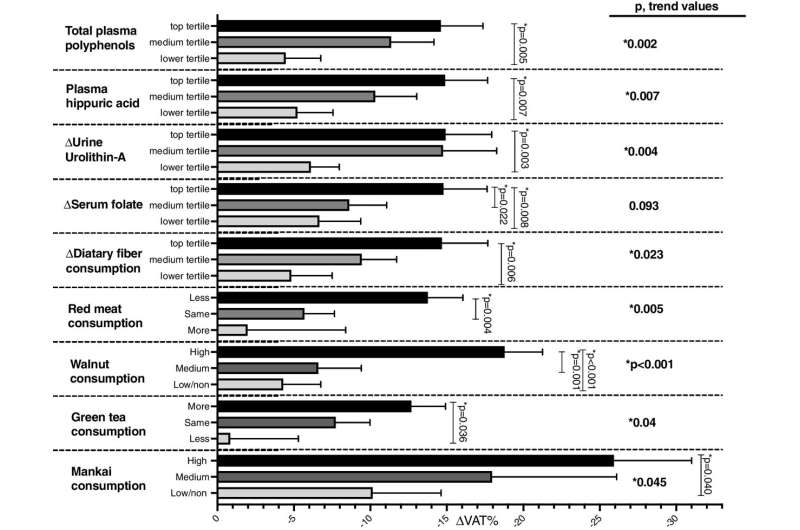
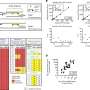
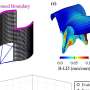
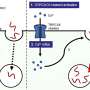
Multivariate models for the assessment of the associations between nutritional components of the green-MED diet with changes in VAT% adjusted for age and sex. Mankai consumption was adjusted for age and referred to the green-MED group only. Mankai consumption categories (18 months): low/non: ≤ 1/week, medium: 2–3/week, and high: > 3/week; walnut consumption categories (18 months): low/non: 0 to 1–3 times/month, medium: 1–2/week to 3–4/week, and high: more than 5–6/week; serum folate tertiles (of 18-month change in serum folate, ng/dL): lower ≤ − 0.41, medium − 0.40 to 1.46, and top ≥ 1.47; fiber consumption tertiles (18-month change, g): lower ≤ − 6.73, medium − 6.72 to − 0.17, and top ≥ − 0.16; plasma polyphenol tertiles (18 months, mg/L): lower ≤ 0.23, medium 0.24 to 0.47, and top ≥ 0.48; specific polyphenols (urine and plasma) and VAT change after 18 months of intervention adjusted for age and sex: urine urolithin-A delta 18 months compared to baseline (log2) tertiles: T1 ≤ 0, T2 = 0 to 4.92, and T3 = 4.92+. r = − 0.241, p < 0.001, q = 0.00036 (MC -139 metabolites). Plasma Hippuric-acid tertiles (time18, mg/L): T1 ≤ 0.21, T2 = 0.21 to 0.44, and T3 = 0.44+. *Significant differences between the groups at the 0.05 level. VAT, visceral adipose tissue. Credit: BMC Medicine (2022). DOI: 10.1186/s12916-022-02525-8
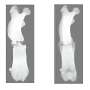
Following the green Mediterranean diet significantly reduces visceral adipose tissue, a type of fat around internal organs that is much more dangerous than the extra "tire" around your waist. Recently, researchers compared the green Mediterranean diet to the traditional Mediterranean diet and a non-Mediterranean healthy diet in a large-scale clinical interventional trial—the DIRECT PLUS. Subsequent analysis found that the green Mediterranean diet reduced visceral fat by 14%, the Mediterranean diet by 7% and the non-Mediterranean healthy diet by 4.5%. The study was published in BMC Medicine.
Reducing visceral fat is considered the true goal of weight loss, as it is a more important indicator than a person's weight or the circumference of their waist. Visceral fat aggregates over time between organs, and produces hormones and poisons linked to heart disease, diabetes, dementia and premature death.
The research was led by Prof. Iris Shai of Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, Israel—also an adjunct Professor from the Harvard School of Public Health, and an Honorary Professor, University of Leipzig, Germany—together with her doctoral student Dr. Hila Zelicha and Italian, German, and American colleagues.
The DIRECT-PLUS trial research team was the first to introduce the concept of the green Mediterranean diet. This modified Mediterranean diet is further enriched with dietary polyphenols and is lower in red/processed meat than the traditional Mediterranean diet. On top of a daily intake of walnuts (28 grams), the participants consumed 3-4 cups of green tea/day and 100 grams (frozen cubes) of duckweed green shake/day. The aquatic green plant duckweed is high in bioavailable protein, iron, B12, vitamins, minerals, and polyphenols and substituted meat intake.
The team has shown in previous studies that the green Mediterranean diet has a variety of salutary effects ranging from the microbiome to age-related degenerative diseases.
A group of 294 participants took part in the 18-month long trial.
"A healthy lifestyle is a strong basis for any weight loss program. We learned from the results of our experiment that the quality of food is no less important than the number of calories consumed and the goal today is to understand the mechanisms of various nutrients, for example, positive ones such as the polyphenols, and negative ones such as empty carbohydrates and processed red meat, on the pace of fat cell differentiation and their aggregation in the viscera," says Prof. Shai.
"A 14% reduction in visceral fat is a dramatic achievement for making simple changes to your diet and lifestyle. Weight loss is an important goal only if it is accompanied by impressive results in reducing adipose tissue," notes Dr. Hila Zelicha.
More information: Hila Zelicha et al, The effect of high-polyphenol Mediterranean diet on visceral adiposity: the DIRECT PLUS randomized controlled trial, BMC Medicine (2022). DOI: 10.1186/s12916-022-02525-8
Journal information: BMC Medicine
Provided by Ben-Gurion University of the Negev