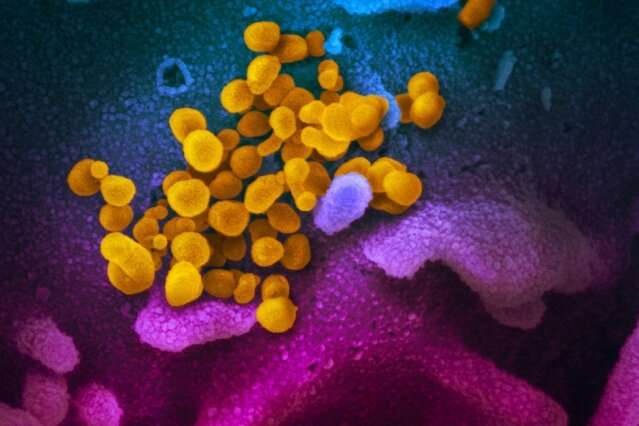
This scanning electron microscope image shows SARS-CoV-2 (yellow)—also known as 2019-nCoV, the virus that causes COVID-19—isolated from a patient, emerging from the surface of cells (blue/pink) cultured in the lab. Credit: NIAID-RML
People with COVID-19 symptoms in one of China's largest cities can now go to work "as normal", state media reported Monday, a dramatic reversal in a country where a single case could previously send thousands into lockdown.
The world's most populous nation is unwinding years of hardline coronavirus policy, with COVID spreading rapidly in the wake of the official end of mass lockdowns, testing and quarantines.
And with authorities admitting the outbreak is "impossible" to track, the southern megacity of Chongqing—home to around 32 million people—became one of the first parts of China to let people work normally even with visible symptoms, the Chongqing Daily reported Monday, citing a notice from municipal authorities.
The notice, issued Sunday, said that "mildly symptomatic" government, party and state workers "can work as normal after undertaking personal protections in accordance with their physical conditions and needs of their jobs".
It also urged residents not to take virus tests "unnecessarily" or require people to show a negative result, with exceptions for certain facilities such as care homes, schools and prisons.
Local governments across China have generally encouraged people to isolate at home while recovering from the disease—a dramatic shift from the previous policy of herding people into state quarantine facilities.
On Sunday, eastern Zhejiang province—a major economic hub home to more than 60 million people—said those with mild symptoms could "continue to work, if need be, on the prerequisite of taking personal protections".
Authorities have stuck to their guns despite evidence that some hospitals and crematoriums are struggling with spiking cases and deaths, as well as fears of a wave of infections in underdeveloped rural areas during the upcoming public holidays.
Visits to hospitals and clinics surged in the days following China's lifting of restrictions, though the World Health Organization said the virus was already spreading widely in the country as "the control measures in themselves were not stopping the disease".
Cities and provinces across China have been forced to adjust their public health offerings as the country learns to coexist with the virus for the first time.
In the eastern city of Suzhou, authorities have hurriedly converted testing sites into makeshift stations for fever treatment, according to state media.
Other cities, including the capital Beijing, have handed out free medical kits to some residents and urged patients to choose online consultations instead of visiting hospitals, state media reported.
© 2022 AFP