Researchers use metabolomics to discover potential biomarkers of hepatocellular carcinoma
A new research paper titled "Essential amino acids as diagnostic biomarkers of hepatocellular carcinoma based on metabolic analysis" has been published in Oncotarget.
Metabolomics, defined as the comprehensive identification of all small metabolites in a biological sample, has the power to shed light on phenotypic changes associated with various diseases, including cancer.
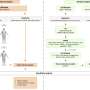
In the current study, researchers from Tokushima University Graduate School, Keio University and Kumamoto University used metabolomics to discover potential biomarkers of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The team investigated the metabolomes of tumor and non-tumor tissue in 20 patients with primary HCC using capillary electrophoresis-time-of-flight mass spectrometry. They also analyzed blood samples taken immediately before and 14 days after hepatectomy to identify associated changes in the serum metabolome.
The researchers explain, "In the present study, we sought to discover reliable metabolomic biomarkers for HCC diagnosis by elucidating metabolic alterations in primary HCC tumor tissue compared with non-tumor tissue, and additionally by investigating the serum metabolomic profiles before and after curative hepatectomy."
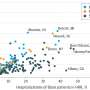
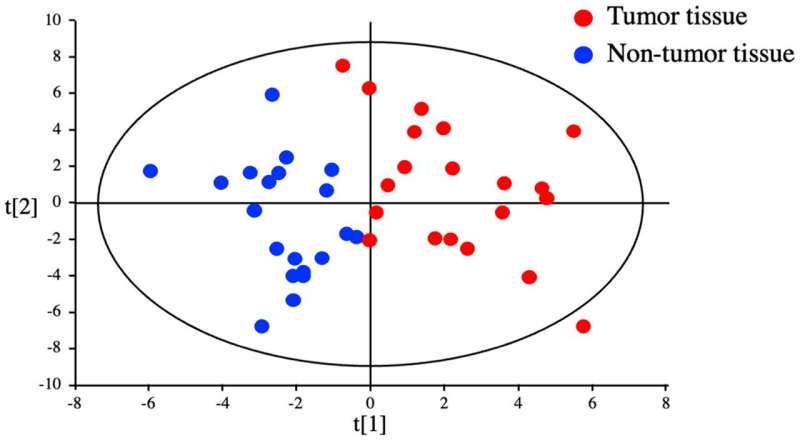
Marked changes were detected in the different quantity of 61 metabolites that could discriminate between HCC tumor and paired non-tumor tissue and additionally between HCC primary tumors and colorectal liver metastases. Among the 30 metabolites significantly upregulated in HCC tumors compared with non-tumor tissues, 10 were amino acids, and 7 were essential amino acids (EAA) (leucine, valine, tryptophan, isoleucine, methionine, lysine, and phenylalanine).
Similarly, the serum metabolomes of HCC patients before hepatectomy revealed a significant increase in 16 metabolites, including leucine, valine, and tryptophan. The results of this study revealed striking differences in the metabolomes of HCC tumor tissue compared with non-tumor tissue, and identified the essential amino acids leucine, valine, and tryptophan as potential metabolic biomarkers for HCC.
"In this study, the major findings were (i) the metabolomic profile of HCC tumors differs not only compared with matched non-tumor liver tissue but also with CRLM tissue, (ii) the serum metabolome of HCC patients is altered by hepatectomy, and (iii) the three EAAs leucine, valine, and tryptophan are candidate metabolomic biomarkers for hepatocarcinogenesis. Notably, however, we found that the metabolic profiles of HCC tumor tissues of differing etiologies (HBV/HCV infection) could not be distinguished, nor could the profiles of non-tumor liver tissue from any of the patient subgroups," the researchers conclude.
More information: Yuji Morine et al, Essential amino acids as diagnostic biomarkers of hepatocellular carcinoma based on metabolic analysis, Oncotarget (2022). DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.28306