This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
reputable news agency
proofread
Postoperative restrictive opioid prescription protocol feasible for most patients
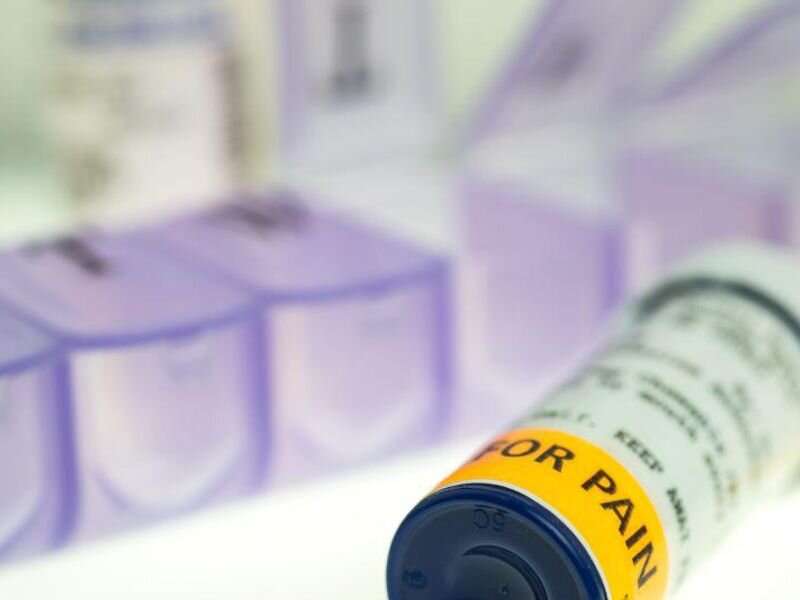
Implementation of a restrictive opioid prescription protocol (ROPP)—prescribing an opioid supply of three or fewer days—to surgical patients after hospital discharge is feasible for most patients, according to a study published online Jan. 5 in JAMA Oncology.
Emese Zsiros, M.D., Ph.D., from the Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center in Buffalo, New York, and colleagues assessed whether postsurgical acute pain across different surgical subspecialties can be managed effectively after hospital discharge with an opioid supply of three or fewer days. The analysis included 2,017 in the pre-ROPP group (Aug. 1, 2018, to Jan. 31, 2019) and 2,051 in the post-ROPP group (Feb. 1, 2019, to July 31, 2019).
The researchers found that after implementation of the ROPP, mean opioid prescription days decreased from a mean of 3.9 days to 1.9 days, with ROPP implementation associated with a 45 percent decrease in prescribed opioids after surgery (mean, 157.22 mean morphine milligram equivalents [MME] before ROPP versus 83.54 MME after ROPP). Fewer refills were requested among patients in the post-ROPP cohort (17.9 versus 20.9 percent in the pre-ROPP cohort). Following ROPP implementation, the conversion rate to chronic opioid use decreased among both opioid-naive patients with cancer (11.3 to 4.5 percent) and those without cancer (6.1 to 2.7 percent).
"The findings suggest that prescription of an opioid supply of three or fewer days is feasible for most postsurgical patients and may be associated with decreased chronic opioid use," the authors write.
More information: Emese Zsiros et al, Postoperative Restrictive Opioid Protocols and Durable Changes in Opioid Prescribing and Chronic Opioid Use, JAMA Oncology (2023). DOI: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2022.6278
Copyright © 2022 HealthDay. All rights reserved.