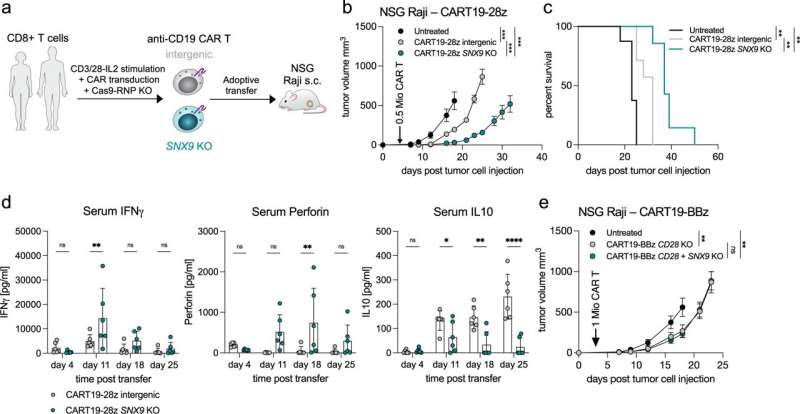
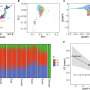
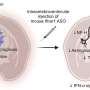
Deletion of SNX9 improves CAR T cell anti-tumor efficacy. a Schematic representation of the CAR T cell transfer experiments. Healthy donor human CD8 T cells are stimulated ex vivo and lentivirally transduced with an anti-human-CD19(FMC63vH)-CD28-CD3zeta-T2A-copGFP CAR construct and electroporated with Cas9-crRNA-tracrRNA complexes to generate SNX9 KO cells and intergenic controls. These cells are then transferred to NSG mice with subcutaneous Raji tumors (CD19+). b Tumor volume in mm3 of NSG mice treated 3 days post Raji tumor injection by i.v. transfer of 0.5 Mio human CD8 anti-CD19-28z CAR T cells with or without SNX9 KO (mean and SEM). Statistics are pairwise 2-way ANOVAs followed by Bonferroni correction. n = 8 animals for untreated of n = 2 experiments. n = 7 mice for CART-treated mice of n = 1 experiment. Experiment was replicated with similar results with higher CART numbers. c Survival of the NSG mice in 5b until humane endpoint of 1500mm3 tumor size. Statistics are log-rank Mantel-Cox tests followed by Bonferroni correction. (b and c): n = 8 for untreated, n = 7 for intergenic and SNX9 KO CAR T conditions. d Human cytokines measured by Legendplex (Biolegend) in the serum of Raji-bearing NSG mice treated with anti-CD19-28z CAR T cells with and without SNX9 KO. Statistics are paired-2-way ANOVA with Holm-Sidak correction. n = 6 mice per condition. Mean and SD are shown. e Tumor volume in mm3 (mean and SEM) of NSG mice treated 3 days post Raji tumor injection by i.v. transfer of 1 Mio human CD8+ CD28 KO anti-CD19-BBz CAR T cells with or without SNX9 KO. n = 6 for intergenic and SNX9 KO, n = 8 for untreated. Statistics are 2-way ANOVAs followed by Bonferroni correction. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001. Credit: Nature Communications (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-35583-w
A tough battle requires endurance. This is also true for white blood cells as they tackle cancer—or more specifically for T lymphocytes or T cells, a group of white blood cells involved in the immune system's fight against cancer cells. However, T cells can become exhausted during this fight.
Researchers from the Department of Biomedicine at the University of Basel and University Hospital Basel recently identified a gene that seems to contribute to this exhaustion. The findings of their research project were published in the journal Nature Communications.
T lymphocyte exhaustion has been a known problem for around 20 years. After a chronic exposure to tumor cells, T cells enter a state of exhaustion and become less effective: while they continue to recognize the hostile tumor cells, they produce fewer substances to eliminate them. In addition, they can no longer develop into memory T cells, which are important in supporting the immune response.
This exhaustion therefore also impacts on the effectiveness of immunotherapies, which are based on stimulating the body's own immune defenses against cancer cells. "This also applies to cell therapies to tackle cancer: even if 'new' T cells are injected into patients, the exhaustion remains a problem," explains Alfred Zippelius, co-author of the study.
Fine-tuning
The research group therefore tried to better understand the mechanisms leading to T cell exhaustion. They developed a model based on human tumor cells and produced exhausted lymphocytes, similar to those found in the tumors of patients.
The team then examined a variety of genes by inactivating them individually using the CRISPR/Cas9 method. This enabled them to identify a gene regulating T cell exhaustion. T cells remain functional when this gene—known as SNX9—is inactivated, even when they are in the vicinity of a tumor over a longer period.
"The SNX9 gene seems to increase the short-term immune response, which can prove important in situations in which every hour counts to tackle a disease. In the case of our experiment, however, suppressing the SNX9 gene enabled finer adjustment of immune cell activity by reducing excessive stimulation signals. The T cells' activity was therefore conserved over a longer period," explains Marcel Trefny, lead author of the study.
The study also found that rather than simply dying after doing their job, the T cells developed into memory T cells more frequently. "The discovery of the role of this gene opens up new approaches for more efficient immunotherapies," says Alfred Zippelius.
These findings are promising, as there is a lack of targets to prevent T cell exhaustion and most experiments to characterize such targets have been performed in mouse cells. However, the therapeutic application of this new approach must now be clinically tested to find out whether the absence of this gene can cause adverse effects.
More information: Marcel P. Trefny et al, Deletion of SNX9 alleviates CD8 T cell exhaustion for effective cellular cancer immunotherapy, Nature Communications (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-35583-w
Journal information: Nature Communications
Provided by Swiss National Science Foundation