This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Cases and transmission of highly contagious fungal infections see dramatic increase between 2019 and 2021

A study of national surveillance data found that cases of Candida auris, a highly contagious fungal infection, rose drastically between 2019 and 2021 reflecting increased transmission. The researchers also noted an increase in echinocandin-resistant cases and evidence of transmission, which is particularly concerning because echinocandins are first-line therapy for invasive Candida infections, including C auris.
These findings emphasize that improved detection and infection control practices are urgently needed to prevent the spread of C auris. The report is published in Annals of Internal Medicine.
Since being initially reported in the United States in 2016, the emerging fungus Candida auris has continued to cause illness and death nationwide. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) rated C auris as an "urgent threat," the highest level of concern, because it is often multidrug-resistant; spreads easily in health care facilities; and can cause severe, invasive infections with high mortality rates. Most transmission occurs in healthcare facilities, especially among residents of long-term care facilities or among persons with indwelling devices or mechanical ventilators.
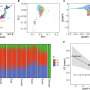
Researchers from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention used national surveillance data on clinical and screening C auris cases reported to state and local health departments and the CDC to describe recent changes in the U.S. epidemiology of C auris between 2019 and 2021. They also examined data from CDC's Antimicrobial Resistance Laboratory Network (AR Lab Network). The data showed that the percentage increase in clinical cases grew each year, from a 44 percent increase in 2019 to a 95 percent increase in 2021.
They also report that colonization screening volume and screening cases increased in 2021 by more than 80 percent and more than 200 percent, respectively. The number of C auris cases that were resistant to first-line treatment in 2021 was about 3 times that in each of the previous 2 years. According to the authors, the timing of this increased C auris spread and findings from public health investigations suggest it may have been exacerbated by pandemic-related strain on the health care and public health systems, which included staff and equipment shortages, increased patient burden and disease severity, increased antimicrobial use, changes in patient movement patterns, and poor implementation of non–COVID-19 IPC measures.
More information: Worsening spread of candida auris in the United States, 2019 to 2021, Annals of Internal Medicine (2023). DOI: 10.7326/M22-3469