This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
proofread
Long-term survey reveals worsening death rate for oral cancer in Queensland
A study analyzing 36 years of cancer data has revealed a rising incidence and a worsening death rate for oral cancer in Queensland.
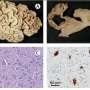
Peter Thomson, Head of Dentistry at JCU and Professor of Oral and Maxillofacial Sciences, was part of a team that examined data for oral squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) cases diagnosed between 1982 and 2018 in Queensland, covering almost 9,900 patients.
Professor Thomson said SCC is a lethal and deforming disease of rising incidence.
"Although this cancer is largely preventable by eliminating risky tobacco and alcohol behavior, five-year survival rates remain around 50%, primarily due to the late diagnosis of advanced-stage disease," he said.
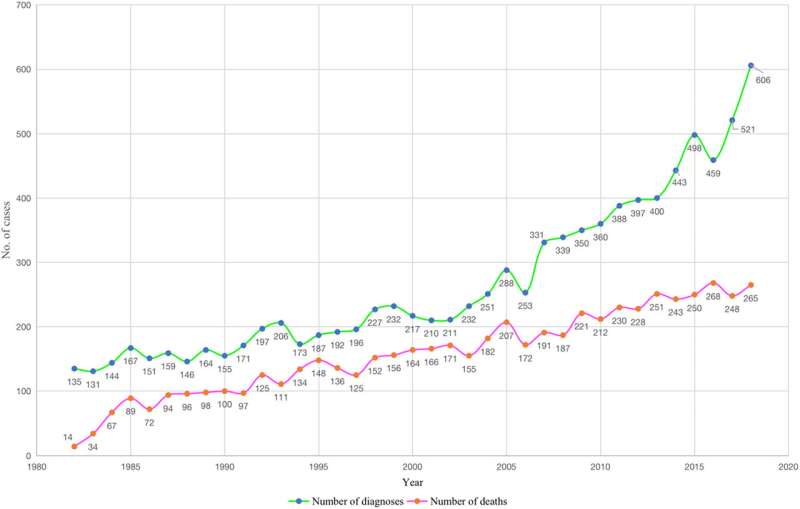
The study aimed to characterize the Queensland population at risk of oral SCC development. It found mean age at diagnosis was 64.55 years and that over the 36-year study period the number of diagnoses increased 4.49-fold, while the number of deaths increased 19.14-fold.
"It's notable that 59% of the people in the dataset were deceased. That's alarming, even though precise cause of death was not always available," said Professor Thomson.
He said low socio-economic status, regional and remote location and Indigenous status are associated with head and neck cancer in general.
"Tobacco and alcohol misuse, diet and nutritional deficiencies, low socio-economic status and human papillomavirus (HPV) infection may be of most relevance in the Queensland population and warrant further study," said Professor Thomson.
He said studies are now underway to sharpen the definition of the socio-demographic and geographic profile of the high-risk population in Queensland.
"Early diagnosis of oral SCC improves clinical outcomes and long-term patient survival, but there are no oral cancer screening programs in Australia. Profiling the at-risk population will enable us to target identified groups with information and possibly earlier intervention," said Professor Thomson.
The study is published in the Journal of Oral Pathology & Medicine.
More information: Aria Sun et al, Oral cancer in Australia: Rising incidence and worsening mortality, Journal of Oral Pathology & Medicine (2023). DOI: 10.1111/jop.13421