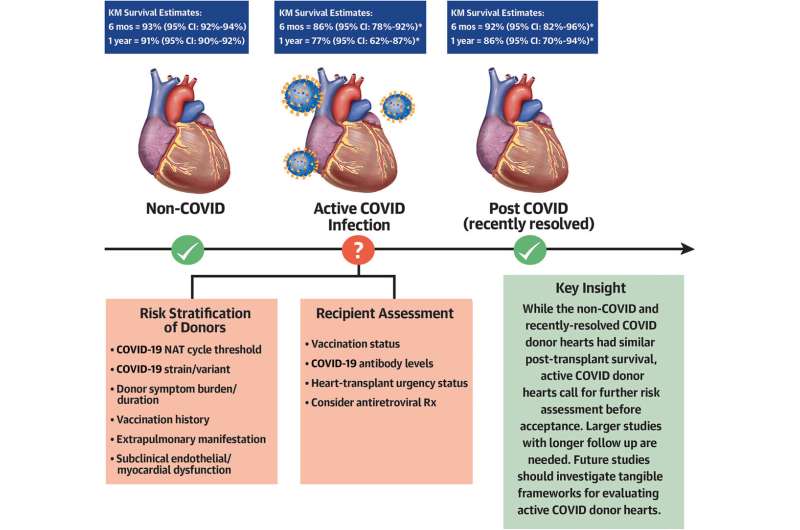
Graphical abstract. Credit: Journal of the American College of Cardiology (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.jacc.2023.04.022
A team of medical researchers from Montefiore Medical Center and Albert Einstein College of Medicine in New York has found that mortality rates are higher for transplant patients receiving a new heart from a person infected with the SARS-CoV-2 virus than from those not infected. In their study, reported in Journal of the American College of Cardiology, the group analyzed data in the United Network for Organ Sharing (UNOS) database related to COVID-19.
Prior autopsy research has shown that while transmissible SARS-CoV-2 viruses are generally limited to those residing in the respiratory tract, proteins tied to the virus are found in other parts of the body, including the heart. The team on this new effort explored the impact of heart donations from COVID-19-infected patients who die from other causes (most often head trauma).
The team analyzed data in UNOS, looking for incidences of heart donors who were found also to have been infected with the SARS-CoV-2 virus, for the period May of 2020 to June 2022. They also extracted data for donors who had experienced an infection prior to donation but who had had time to recover before their death.
In all, the research team found 150 donors who had been infected at the time of their death and 87 who had died not long after recovering from an infection. They also pulled data for similar patient types for donors with no history of infection.
In looking at their data, they found that for patients who had received a heart from an infected donor, the mortality rate was 13.8% at six months, compared to 4.9% for those who had not been infected. At one year, the rates were 23.2% and 9.2% respectively. The researchers also found that rate differences in patients receiving hearts from donors who had recovered from their infections before donating were nearly identical to those who had received a heart from someone who had never been infected.
The team concludes by suggesting that donors should be tested for COVID-19 before heart donation, or any other organ, based on their findings.
More information: Shivank Madan et al, Early Outcomes of Adult Heart Transplantation From COVID-19 Infected Donors, Journal of the American College of Cardiology (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.jacc.2023.04.022
Journal information: Journal of the American College of Cardiology
© 2023 Science X Network