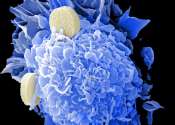
Promising compound kills range of hard-to-treat cancers by targeting a previously undiscovered vulnerability
A compound, developed by a team including scientists from The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio, kills a range of hard-to-treat cancer types in petri dishes and animal models by targeting a previously ...
Jun 2, 2022
0
1092