A brand new cocktail to fight HIV
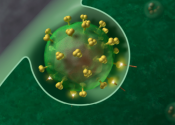
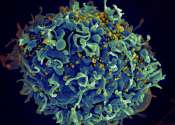
Researchers at the University of Montreal Hospital Research Centre (CRCHUM) and Yale University have succeeded in reducing the size of the HIV reservoir in humanized mice by using a "molecular can opener" and a combination ...
May 20, 2021
0
4861