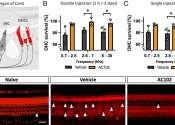
New large-scale study results add to evidence that vestibular loss increases dementia risk
Existing research shows a link between hearing loss and the risk of dementia, and a new study adds to growing evidence that vestibular loss can increase dementia risk as well. Results from this work, by a team from the Korea ...