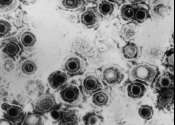
Herpes simplex virus 1 (HWJ-1)
Herpes simplex virus 2 (HWJ-2)
Herpes simplex virus 1 and 2 (HSV-1 and HSV-2) are two species of the herpes virus family, Herpesviridae, which cause infections in humans. Eight members of herpes virus infect humans to cause a variety of illnesses including cold sores, chickenpox or varicella, shingles or herpes zoster (VZV), cytomegalovirus (CMV), and various cancers, and can cause brain inflammation (encephalitis). All viruses in the herpes family produce life-long infections.
They are also called Human Herpes Virus 1 and 2 (HHV-1 and HHV-2) and are neurotropic and neuroinvasive viruses; they enter and hide in the human nervous system, accounting for their durability in the human body. HSV-1 is commonly associated with herpes outbreaks of the face known as cold sores or fever blisters, whereas HSV-2 is more often associated with genital herpes.
An infection by a herpes simplex virus is marked by watery blisters in the skin or mucous membranes of the mouth, lips or genitals. Lesions heal with a scab characteristic of herpetic disease. However, the infection is persistent and symptoms may recur periodically as outbreaks of sores near the site of original infection. After the initial, or primary, infection, HSV becomes latent in the cell bodies of nerves in the area. Some infected people experience sporadic episodes of viral reactivation, followed by transportation of the virus via the nerve's axon to the skin, where virus replication and shedding occurs.
Herpes is contagious if the carrier is producing and shedding the virus. This is especially likely during an outbreak but possible at other times. There is no cure yet, but there are treatments which reduce the likelihood of viral shedding.