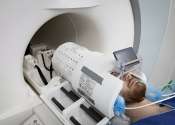
World's most powerful MRI scans first images of human brain
The world's most powerful MRI scanner has delivered its first images of human brains, reaching a new level of precision that is hoped will shed more light on our mysterious minds—and the illnesses that haunt them.
Apr 2, 2024
0
128