U.S. scientists have identified four genes that interact with serious obstetric complications to increase the risk for schizophrenia.
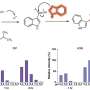
National Institute of Mental Health researchers in Bethesda, Md., examined 13 genes believed to play a role in the development of schizophrenia. All of the genes also play a role in supplying blood to the brain, or are influenced by hypoxia -- a condition in which insufficient oxygen is present for proper cellular functioning.
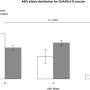
A subset of individuals tested had experienced at least one serious obstetric complication, many having the potential to lead to hypoxia.
The researchers determined individuals who had four specific genetic variations, and who also had experienced at least one serious obstetric complication, were significantly more likely to develop schizophrenia as adults.
The study appears in the online issue of the journal Molecular Psychiatry.
Copyright 2008 by United Press International