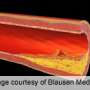
A single scan could diagnose the cause of foot pain better and with less radiation exposure to the patient than other methods, according to a study in the March 2015 issue of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine. Imaging with 18F-fluoride positron emission tomography/magnetic resonance imaging (PET/MR), compared to 18F-fluoride positron emission tomography/computed topography (PET/CT), provides more diagnostic information with higher diagnostic certainty.
Foot pain is a common problem in the daily routine of any orthopedic surgeon. It can be a clinical symptom of many different issues, from stress fractures to tumors. Multiple imaging modalities are available to help diagnose specific types of foot pain, but no one modality is useful for effectively diagnosing a wide range of causes. Imaging with 18F-fluoride PET is highly sensitive tool but has low specificity for detection of metabolically active benign bone disease, while MR imaging provides excellent soft-tissue contrast and high resolution which helps in specifying a diagnosis. Thus, combined, PET/MR can offer an important tool for the sensitive diagnosis of foot pathologies.
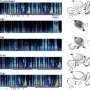
In "Evaluation of 18F-Fluoride PET/MR and PET/CT in Patients with Foot Pain of Unclear Cause," researchers compared the quality and diagnostic performance of 18F-fluoride PET/MR to those of 18F-fluoride PET/CT in 22 patients for whom the specific diagnosis was inconclusive after clinical examination and radiography. The results of overall image quality showed that PET/MR was significantly superior to PET/CT, with an overall excellent image quality score of 3.0/3 points in all PET/MR datasets, while PET/CT achieved 2.3 out of 3 possible points.
"In our study, 18F-fluoride PET/MR provided more diagnostic information at a higher diagnostic certainty compared to 18F-fluoride PET/CT in patients with foot pain of unclear cause," states Isabel Rauscher, corresponding author of the study. "Besides information on bone metabolism, it provides additional diagnostic relevant findings from soft-tissue and bone marrow pathology (e.g., bone marrow edema, ganglion cysts or tenosynovitis) compared to PET/CT." Also, since MR involves no radiation and the scan allows a longer PET acquisition time, the patient's exposure is lower than with CT.
Journal information: Journal of Nuclear Medicine
Provided by Society of Nuclear Medicine