Credit: CC0 Public Domain
In a new study in the Journal of Cognitive, Affective & Behavioral Neuroscience researchers from the University of Surrey have discovered a link between meditation and how individuals respond to feedback.
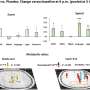
Participants in the study, a mixture of experienced, novice and non-meditators, were trained to select images associated with a reward. Each pair of images had varying probabilities of a reward e.g. images that result in a reward 80 per cent of the time versus those that result in a reward 20 per cent of the time. Participants eventually learnt to select the pairing with the higher outcome.
Researchers found that participants who meditated were more successful in selecting high-probability pairings indicating a tendency to learn from positive outcomes, compared to non – meditators who learned the pattern via low-probability pairings suggesting a tendency to learn from negative outcomes.
During the study participants were connected to an EEG, a non-invasive method that records electrical patterns in the brain. Results from the EEG found that while all three groups responded similarly to positive feedback, the neurological response to negative feedback was highest in the non-meditation group, followed by the novice group and then by the experienced meditation group. These results indicate that the brains of meditators are less affected by negative feedback, and that this may be a result of altered dopamine levels caused by meditation.
Previous studies in this field on patients with Parkinson's disease, where dopamine levels are severely reduced, have shown that the compound affects how people respond to feedback, indicating that dopamine is integral to how we learn and process information. The present study suggests that meditation may present a way to affect levels of dopamine in the brain and the way humans deal with positive and negative feedback.
Paul Knytl, lead author and Ph.D. candidate in psychology at the University of Surrey, said: "Humans have been meditating for over 2000 years, but the neural mechanisms of this practice are still relatively unknown. These findings demonstrate that, on a deep level, meditators respond to feedback in a more even-handed way than non-meditators, which may help to explain some of the psychological benefits they experience from the practice."
Bertram Opitz, Professor in Neuroimaging and Cognitive Neuroscience at the University of Surrey, said: "Meditation is a powerful tool for the body and the mind; it can reduce stress and improve immune function. What we have found is that it can also impact on how we receive feedback, i.e. if we quickly learn from our mistakes or if we need to keep making them before we find the right answer.
"If it is the latter this can impact how individuals perform in the workplace or classroom. Such individuals may benefit from meditation to increase their productivity or prevent them from falling behind in their studies."
More information: Paul Knytl et al. Meditation experience predicts negative reinforcement learning and is associated with attenuated FRN amplitude, Cognitive, Affective, & Behavioral Neuroscience (2018). DOI: 10.3758/s13415-018-00665-0
Journal information: Cognitive, Affective, & Behavioral Neuroscience
Provided by University of Surrey