(HealthDay)—Patients with even nonsevere COVID-19 seek health care frequently within 30 days of diagnosis, according to a study published online Jan. 6 in the Journal of General Internal Medicine.
Brian Z. Huang, Ph.D., from Kaiser Permanente Southern California in Pasadena, and colleagues assessed trends in health care utilization within 180 days for patients diagnosed with COVID-19, and identified patient factors associated with increased health care use. The analysis included 64,011 patients with a test-confirmed COVID-19 diagnosis at a large, integrated health care system from March to September 2020.
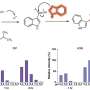
The researchers found that health care utilization was about twice as high for hospitalized patients versus nonhospitalized patients in all time periods. The first 30 days showed the highest average number of visits (hospitalized: 12.3 visits/30 person-days; nonhospitalized: 6.6), which gradually decreased over time. The majority of health care visits were telehealth encounters in the first 30 days (hospitalized: 9.0 visits; nonhospitalized: 5.6 visits), with COVID-19-related diagnoses, COVID-19-related symptoms, and respiratory-related conditions the most prevalent reasons for visits. Higher utilization among hospitalized patients was associated with older age (65 years or older: rate ratio, 1.27), female gender (rate ratio, 1.07), and higher body mass index (≥40: rate ratio, 1.07). For nonhospitalized patients, non-White race/ethnicity, former smoking, and greater number of preexisting comorbidities were also associated with increased utilization.
"Identifying ways to support patients diagnosed with COVID-19 while adequately providing the usual recommended care to our communities will be important as we recover from the pandemic," the authors write.
More information: Abstract/Full Text
Journal information: Journal of General Internal Medicine
Copyright © 2021 HealthDay. All rights reserved.