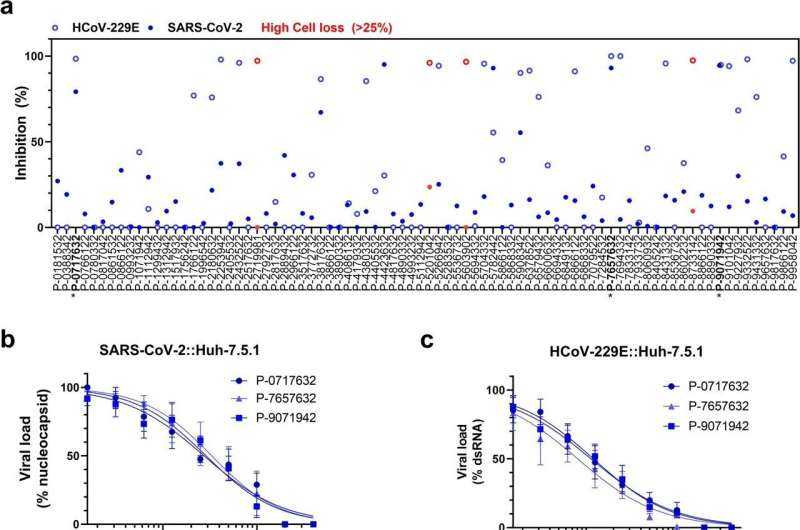
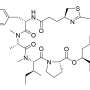
Screening of GSK3β inhibitors. a High-content screen of SARS-CoV-2 (full circles) and HCoV-229E (empty circles) infected Huh-7.5.1 cells with the Takeda GSK3β-focused library at a single dose of 10 μM. Inhibition was interpolated to both a non-infected control and an infected, untreated control, quantifying intracellular dsRNA. Cell loss was assessed to avoid quantifying small populations and compounds resulting in > 25% cell loss are marked in red. Compounds marked with an asterisk were further pursued. The Z’ of two independent screens were 0.54 and 0.74 for SARS-CoV-2 and 0.68 for HCoV-229E. b-c Dose-response validation of compounds of interest. Each dose is an average of four independent experiments, error bars show SEM. Viral load of SARS-CoV-2 (b) was determined by measuring intracellular N protein and viral load of HCoV-229E (c) by measuring dsRNA. d Western analysis of SARS-CoV-2 N protein, representative blot of four independent experiments. Credit: Molecular Biomedicine (2022). DOI: 10.1186/s43556-022-00111-1
Researchers at UBC's Life Sciences Institute have identified a compound that shows early promise at halting infections from a range of coronaviruses, including all variants of SARS-CoV-2 and the common cold.
The findings, published this week in Molecular Biomedicine, reveal a potential path toward antiviral treatments that could be used against many different pathogens.
"Beyond COVID-19, there are many different types of coronaviruses that can cause serious and sometimes fatal disease, and even more are likely to emerge in the future," says Dr. Yossef Av-Gay, an infectious disease professor in UBC's faculty of medicine and the study's senior author.
"We're working toward treatments that can be broadly effective against all types of coronaviruses so that we can respond to not only current health challenges, but also future pandemic threats. Identifying this compound and the pathway by which it works to stop viruses is an important step in that direction."
Targeting the host, not the virus
The researchers credit the compound's broad effectiveness to the unique way it works. Rather than targeting the virus itself, the compound targets a human cellular process that coronaviruses use to replicate.
Since viruses can't reproduce on their own, they rely on protein-synthesis pathways in host cells to create copies of themselves. In the case of coronaviruses, they use a human enzyme called GSK3 beta that exists in all human cells.
"We found that coronaviruses hijack this human enzyme and use it to edit the protein that packs its genetic material," says Dr. Tirosh Shapira, a postdoctoral fellow at UBC's faculty of medicine and the study's first author. "This compound blocks GSK3 beta, which in turn, stops the virus from reproducing and maturing its proteins."
The compound is part of a broader family of experimental drugs known as GSK3 inhibitors. Since the late 1990s, scientists across academia and industry have been studying GSK3 inhibitors for their potential as treatments for a number of diseases, including diabetes, Alzheimer's and cancer.
"By targeting this cellular pathway, rather than the virus itself, we see broad activity against multiple pathogens. We're also acting on a pathway that is so far immune to changes between variants and different coronaviruses," says Dr. Shapira.
Future-proof treatments
To identify the compound, the research team screened a library of nearly 100 known GSK3 inhibitors, provided through a collaboration between UBC and Takeda Pharmaceutical Company in Japan. The compounds were tested in cell and tissue models infected with SARS-CoV-2 and the common cold virus.
The testing yielded multiple GSK3 inhibitors that showed a high level of effectiveness against the coronaviruses and low toxicity to human cells. The leading compound, identified as T-1686568, inhibited both SARS-CoV-2 and the common cold virus, the main criteria the authors used in the search for broad-spectrum protection.
"While these are early days, it's encouraging to see broad levels of effectiveness in tissue models," says Dr. Shapira. "Because these compounds require many years of testing and regulatory approval before they can potentially reach patients, we need to be thinking about long-term applications and how this could apply broadly to future viruses and variants."
The research was conducted at UBC FINDER, a level-3 biocontainment facility at UBC where researchers are working with highly infectious pathogens with an aim to develop future treatments.
"We're not just fighting SARS-CoV-2, we're looking ahead at what's next," says Dr. Shapira. "We're focused on identifying future-proof treatments for variants and viruses that emerge down the road and rely on the same cellular mechanisms to grow and infect."
More information: Tirosh Shapira et al, Inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase-3-beta (GSK3β) blocks nucleocapsid phosphorylation and SARS-CoV-2 replication, Molecular Biomedicine (2022). DOI: 10.1186/s43556-022-00111-1
Provided by University of British Columbia