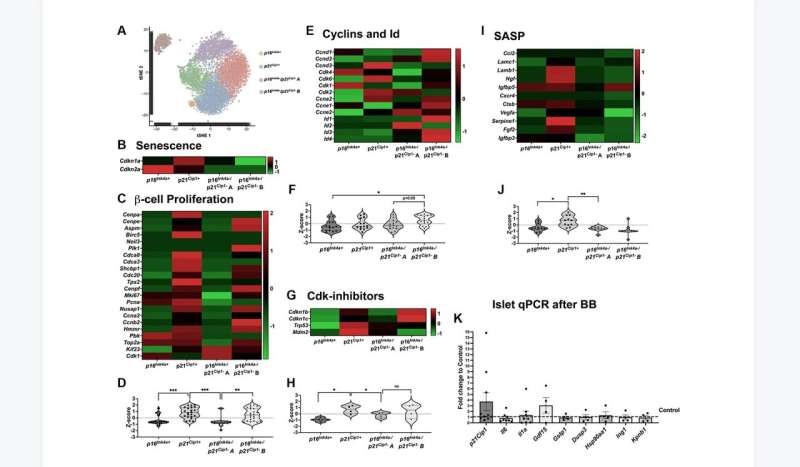
p16Ink4a-expressing cells do not proliferate or secrete SASP compared to other senescent cells. Credit: 2023 Bahour et al.
A new research paper titled "Clearance of p16Ink4a-positive cells in a mouse transgenic model does not change β-cell mass and has limited effects on their proliferative capacity" has been published in Aging.
Type 2 diabetes is partly characterized by decreased β-cell mass and function, which have been linked to cellular senescence. Despite the low basal proliferative rate of adult β-cells, they can respond to growth stimuli, but this proliferative capacity decreases with age and correlates with increased expression of senescence effector, p16Ink4a.
In a new study, researchers from the Joslin Diabetes Center at Harvard Medical School hypothesized that selective deletion of p16Ink4a-positive cells would enhance the proliferative capacity of the remaining β-cells due to the elimination of the local senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP).
"We aimed to investigate the effects of p16Ink4a-positive cell removal on the mass and proliferative capacity of remaining β-cells using INK-ATTAC mice as a transgenic model of senolysis," the researchers write.
Clearance of p16Ink4a-positive subpopulation was tested in mice of different ages, males and females, and with two different insulin resistance models: high-fat diet (HFD) and insulin receptor antagonist (S961). Clearance of p16Ink4a-positive cells did not affect the overall β-cell mass. β-cell proliferative capacity negatively correlated with cellular senescence load and clearance of p16Ink4a positive cells in 1-year-old HFD mice improved β-cell function and increased proliferative capacity in a subset of animals. Single-cell sequencing revealed that the targeted p16Ink4a subpopulation of β-cells is non-proliferative and non-SASP producing, whereas additional senescent subpopulations remained contributing to continued local SASP secretion.
"In conclusion, deletion of p16Ink4a cells did not negatively impact beta-cell mass and blood glucose under basal and HFD conditions and proliferation was restored in a subset of HFD mice, opening further therapeutic targets in the treatment of diabetes," the researchers summarize.
More information: Nadine Bahour et al, Clearance of p16Ink4a-positive cells in a mouse transgenic model does not change β-cell mass and has limited effects on their proliferative capacity, Aging (2023). DOI: 10.18632/aging.204483
Provided by Impact Journals LLC