Concurrent use of two immune checkpoint antibodies -- ipilimumab and nivolumab -- may be effective for the treatment of advanced melanoma, according to a proof-of-principal study presented in advance of the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology, held from May 31 to June 4 in Chicago.
(HealthDay)—Concurrent use of two immune checkpoint antibodies—ipilimumab and nivolumab—may be effective for the treatment of advanced melanoma, according to a proof-of-principal study presented in advance of the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology, held from May 31 to June 4 in Chicago.
Jedd D. Wolchok, M.D., Ph.D., from the Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center in New York City, and colleagues enrolled patients who had received no more than three prior treatments. Patients received intravenous nivolumab and ipilimumab concurrently for four doses, followed by nivolumab alone. Additionally, in two other study arms, patients who had undergone prior ipilimumab treatment received only nivolumab.
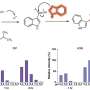
The researchers found that, based on the 37 patients treated with concurrent therapy, the objective response rate was 38 percent. In the three concurrent treatment arms that completed the trial, tumor shrinkage rates were 21, 47, and 50 percent, with the highest rates seen in patients treated with the highest dose of both drugs. The responses to therapy were rapid, with three out of four responding patients doing so within the first three months, which is faster than with single-agent ipilimumab. Thirty percent of patients experienced significant tumor shrinkage of more than 80 percent. Adverse events for concurrent therapy were similar in nature (although some with higher frequency) than those typically seen for the monotherapies and were generally manageable using immunosuppressants.
"The complete and near-complete response rates we're seeing are unprecedented for an immunotherapy in melanoma," Wolchok said in a statement.
Several authors disclosed financial ties to Bristol-Myers Squibb, which funded the study and manufactures ipilimumab and nivolumab.
More information:
Abstract
More Information
Health News Copyright © 2013 HealthDay. All rights reserved.