Social media outlets represent a promising source of information relating to left ventricular assist device treatment for heart failure, but their reliability is hampered by current lack of oversight into content, according to a study published online July 28 in Circulation: Cardiovascular Quality and Outcomes.
(HealthDay)—Social media outlets represent a promising source of information relating to left ventricular assist device treatment for heart failure, but their reliability is hampered by current lack of oversight into content, according to a study published online July 28 in Circulation: Cardiovascular Quality and Outcomes.
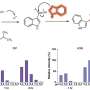
Kristin M. Kostick, Ph.D., from the Baylor College of Medicine in Houston, and colleagues conducted a mixed-method study, including content analysis of social media and principal components analysis of data sites discussing left ventricular assist device treatment. Aspects of interactivity, user-friendliness, appeal, medium, purpose, audience, and accuracy of information were explored.
The researchers found that the appeal and usability of available information was enhanced by higher levels of interactivity (e.g., posting comments), but also introduced greater potential for inaccuracy and inconsistency. Current lack of oversight into the content and quality of information represents a challenge for the reliability of social media as a source of information and social network-based support.
"We conclude that social media outlets constitute a promising source of informational and psychosocial support for patients, caregivers, and candidates, and if used in conjunction with patient-provider dialog, can contribute to informed decision-making by facilitating reflection and discussion of personal concerns, values, and informational needs," the authors write.
More information:
Abstract
Full Text (subscription or payment may be required)
Journal information: Circulation: Cardiovascular Quality and Outcomes
Copyright © 2015 HealthDay. All rights reserved.