Credit: Asociacion RUVID
A team of researchers from the UCH CEU's Biomedical Sciences Institute has tested the efficiency of Bevacizumab, medicine used against cancer and in opthalmology, to treat uveítis, thus stopping the inflammation from spreading.
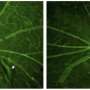
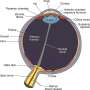
Uveitis is an inflammation of the uvea – the ocular tissue between the sclera and the retina. It can be caused by infections or autoimmune diseases. The uvea provides a majority of the blood supply to the retina, so early treatment for inflammation could be key to preventing consequences in other ocular tissues—if the condition is not treated in time, the inflammation can spread to the vitreous and the retina. Researchers of the Biomedicine Sciences Institute of the Universidad Cardenal Herrera CEU university (UCH CEU) in Valencia have tested the efficiency of Bevacizumab in treating uveitis using an experimental model. The results, which provide a new strategy for treating uveitis and preventing its effects, have been published in Frontiers in Pharmacology.
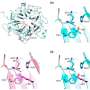
Professor Francisco Bosch, head of the UCH CEU's Biomedical Sciences Institute, says, "Bevacizumab is a medicine used in combined immunotherapy for treating tumours, which also has several ophthalmologic uses for treating ocular diseases such as diabetic retinopathy, macular oedema or glaucoma." The research team of the UCH CEU, headed by doctor Bosch, has studied the medicine's anti-inflammatory capacity and its potential risks regarding toxicity in induced uveitis in an experimental model.
Anti-inflammatory effect
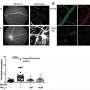
Professor Bosch says, "The cellular and histopathological count results obtained by our team prove the capabilities of the medicine to prevent inflammation, not only of the uvea, but also the retina and the vitreous chamber. And it also makes it possible to rule out the risk of retinal degradation that could be associated to the use of the medicine."
These results also provide relevant data regarding the controversy surrounding the use of injectable medicines with vascular endothelium anti-growth factor, the anti-VEGF. "Even though bevacizumab, commercialised as Avastin, was initially developed to treat several types of cancer, it is commonly used in ophthalmology despite this use not being recommended. Our results verify that in this field, it is as effective and safe as other anti-VEGF medicines such as Lucentis, which was designed specifically for ophthalmologic purposes, but is more expensive," says Dr. Bosch.
More information: Salvador Mérida et al. Bevacizumab Diminishes Inflammation in an Acute Endotoxin-Induced Uveitis Model, Frontiers in Pharmacology (2018). DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00649
Provided by Asociacion RUVID