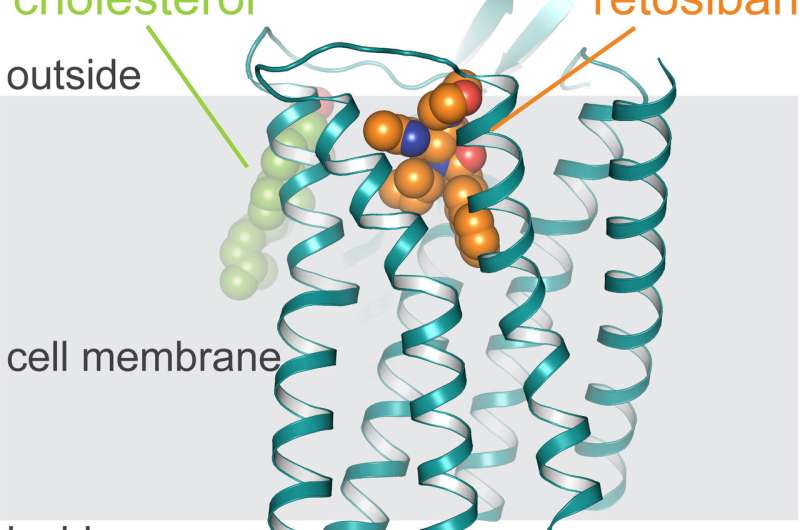
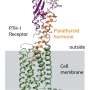
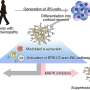
Structure of the oxytocin receptor in the cell membrane (grey), to which retosiban (orange) and cholesterol (green) are bound. Credit: University of Zurich
The so-called "love hormone," oxytocin, is not only involved in strengthening the mother-child relationship and regulating social bonding; it has also been associated with mental health disorders like autism, Asperger's syndrome, social anxiety, and addiction vulnerability. Furthermore, oxytocin triggers the birth process, and is involved in many aspects of sexual reproduction, as well as corresponding disorders. The hormone exerts all these effects by binding to the oxytocin receptor. Substances that target the oxytocin receptor thus have great therapeutic potential for a variety of diseases.
Since its discovery nearly 30 years ago, researchers have tried to develop drugs that bind specifically to the oxytocin receptor. However, conducting such experiments has proved to be very difficult. Except for the hormone oxytocin itself, hardly any drug targeting the oxytocin receptor has been approved for clinical use. A team led by Andreas Plückthun, professor at the Department of Biochemistry of the University of Zurich (UZH), has now determined the detailed three-dimensional structure of the oxytocin receptor bound to the drug candidate retosiban, which was developed for the suppression of preterm labor.
"The elucidation of the oxytocin receptor's structure was an extremely challenging undertaking, which only succeeded thanks to a combination of directed evolution and protein engineering methods we developed over the last few years," says Plückthun. "Understanding the exact three-dimensional interaction of retosiban and the oxytocin receptor at the atomic level serves as the blueprint for developing new therapeutics that regulate the receptor's functioning."
Improved understanding of receptor mechanism
The scientists also made an additional discovery. "To allow efficient propagation of oxytocin-induced signaling, the oxytocin receptor has to interact with two additional substances—cholesterol and magnesium," says Ph.D. candidate Yann Waltenspühl. Determining the exact receptor shape enabled the researchers to identify interaction regions for both of these substances. "The identification of these previously unknown regions fundamentally improves the understanding of the receptor mechanism."
The new findings might also be directly applicable to the very closely related vasopressin receptors. The hormone vasopressin controls the water content of body fluids and the blood pressure, and its receptors are therefore drug targets for the treatment of many diseases, from kidney disease to heart failure. Just like the oxytocin receptor, the vasopressin receptors have also been implicated in autism spectrum disorders. "Our work could thus boost the development of new drugs for a very broad range of widespread and severe human diseases," says Andreas Plückthun.
More information: Crystal structure of the human oxytocin receptor, Science Advances (2020). DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abb5419
Journal information: Science Advances
Provided by University of Zurich